Notoamide-type alkaloid induced apoptosis and autophagy via a P38/JNK signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- PMID: 35519412
- PMCID: PMC9065365
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra03640g
Notoamide-type alkaloid induced apoptosis and autophagy via a P38/JNK signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Abstract
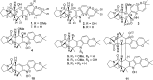
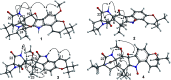
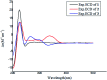
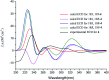
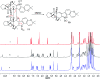
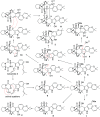
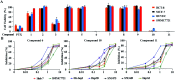
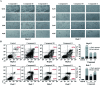
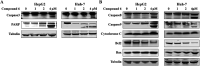
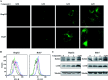
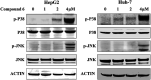
Bioassay-guided fractionation of a coral-associated fungus Aspergillus ochraceus LZDX-32-15 resulted in the isolation of eleven notoamide-type alkaloids, including four new congeners, namely notoamides W-Z (1-4). The structures of the new alkaloids were determined by extensive analyses of spectroscopic data (1D and 2D NMR, HRESIMS), while ECD data were used for the configurational assignment. Three alkaloids (6, 10, 11) exerted potent inhibition against a panel of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 0.42 to 3.39 μM, that are comparable to the data for paclitaxel. Notoamide G (6) inhibited the viability of HepG2 and Huh-7 cells via both apoptosis and autophagy pathways. Notoamide G activated the expression of caspase-3, caspase-8, and caspase-9, in association with the degradation of the downstream gene PARP in a dose-dependent manner, suggesting that notoamide G induced apoptosis via a mitochondrial pathway and a dead receptor-mediated pathway. In addition, notoamide G increased the autophagic vacuole in both HepG2 and Huh-7 cells in a dose-dependent manner after 24 h through the significant upregulation of the key proteins Beclin1 and LC3B. Further investigation revealed that notoamide G promoted P38 and JNK phosphorylation, whereas the total protein of P-38 and JNK was slightly influenced. Accordingly, the antitumor proliferation of notoamide G in HCC cells was mechanistically mediated by apoptosis and autophagy through a P38/JNK signaling pathway, while notoamide G was considered as a potent lead for further development as an antitumor agent.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sclerotiamides C-H, Notoamides from a Marine Gorgonian-Derived Fungus with Cytotoxic Activities.J Nat Prod. 2022 Apr 22;85(4):1067-1078. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.1c01194. Epub 2022 Feb 25. J Nat Prod. 2022. PMID: 35213164 Review.
-
Prenylated notoamide-type alkaloids isolated from the fungus Aspergillus sclerotiorum and their inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and antibacterial activities.Phytochemistry. 2022 Nov;203:113424. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2022.113424. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Phytochemistry. 2022. PMID: 36063866
-
EM-2 inhibited autophagy and promoted G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis by activating the JNK pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021 Jul;42(7):1139-1149. doi: 10.1038/s41401-020-00564-6. Epub 2020 Dec 14. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021. PMID: 33318625 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor 9 signaling promotes autophagy and apoptosis via divergent functions of the p38/JNK pathway in human salivary gland cells.Exp Cell Res. 2019 Feb 15;375(2):51-59. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.12.027. Epub 2019 Jan 3. Exp Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 30610847
-
Piperine functions as a tumor suppressor for human ovarian tumor growth via activation of JNK/p38 MAPK-mediated intrinsic apoptotic pathway.Biosci Rep. 2018 May 31;38(3):BSR20180503. doi: 10.1042/BSR20180503. Print 2018 Jun 29. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29717031 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Specific c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Inhibitor, JNK-IN-8 Suppresses Mesenchymal Profile of PTX-Resistant MCF-7 Cells through Modulating PI3K/Akt, MAPK and Wnt Signaling Pathways.Biology (Basel). 2020 Oct 1;9(10):320. doi: 10.3390/biology9100320. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33019717 Free PMC article.
-
Ethyl Acetate Fraction of Hedyotis diffusa Willd Induces Apoptosis via JNK/Nur77 Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Aug 24;2022:1932777. doi: 10.1155/2022/1932777. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36062172 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative-Stress-Mediated ER Stress Is Involved in Regulating Manoalide-Induced Antiproliferation in Oral Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 16;24(4):3987. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043987. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835397 Free PMC article.
-
Naturally derived indole alkaloids targeting regulated cell death (RCD) for cancer therapy: from molecular mechanisms to potential therapeutic targets.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Sep 14;15(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01350-z. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36104717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Mutually Inspiring Biological and Chemical Synthesis of Fungal Bicyclo[2.2.2]diazaoctane Indole Alkaloids.Chem Rev. 2025 Feb 26;125(4):1718-1804. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.4c00250. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Chem Rev. 2025. PMID: 39927617 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Momin B. Millman A. J. Nielsen D. B. Revels M. Steele C. B. Promising practices for the prevention of liver cancer: a review of the literature and cancer plan activities in the National Comprehensive Cancer Control Program. Cancer Causes Control. 2018;29:1265–1275. doi: 10.1007/s10552-018-1094-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

