Gas-phase degradation of 2-butanethiol initiated by OH radicals and Cl atoms: kinetics, product yields and mechanism at 298 K and atmospheric pressure
- PMID: 35519461
- PMCID: PMC9067059
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra04051j
Gas-phase degradation of 2-butanethiol initiated by OH radicals and Cl atoms: kinetics, product yields and mechanism at 298 K and atmospheric pressure
Abstract
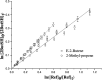
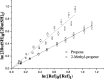
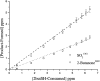
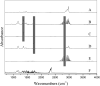
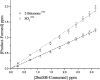
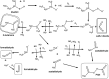
Relative rate coefficients and product distribution of the reaction of 2-butanethiol (2butSH) with OH radicals and Cl atoms were obtained at atmospheric pressure and 298 K. The experiments were performed in a 480 L borosilicate glass photoreactor in synthetic air coupled to a long path "in situ" FTIR spectrometer. The rate coefficients obtained by averaging the values from different experiments were: k OH = (2.58 ± 0.21) × 10-11 cm3 per molecule per s and k Cl = (2.49 ± 0.19) × 10-10 cm3 per molecule per s. The kinetic values were compared with related alkyl thiols and homologous alkyl alcohols, where it was found that thiols react faster with both oxidants, OH radicals and Cl atoms. SO2 and 2-butanone were the major products identified for the reactions of 2-butanethiol with OH radicals and Cl atoms. The product yield of the reaction of 2-butanethiol and OH radicals were (81 ± 2)%, and (42 ± 1)% for SO2 and 2-butanone, respectively. For the reactions of 2-butanethiol with Cl atom, yields of SO2 and 2-butanone were (59 ± 2)% and (39 ± 2)%, respectively. A degradation mechanism was proposed for the pathways that leads to formation of identified products. The product distribution observed indicated that the H-atom of the S-H group abstraction channel is the main pathway for the reaction of OH radicals and Cl atoms with 2-butanethiol.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Li K.-C. Shooter D. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2004;84:749–760. doi: 10.1080/03067310410001729619. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

