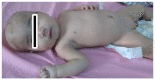
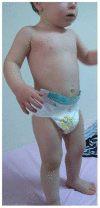
Refeeding Syndrome Developed in a Patient With Kwashiorkor Can Mimic Findings of Mitochondrial Disorder
- PMID: 35519509
- PMCID: PMC9067038
- DOI: 10.1177/11795476221093287
Refeeding Syndrome Developed in a Patient With Kwashiorkor Can Mimic Findings of Mitochondrial Disorder
Abstract
Kwashiorkor is a serious nutritional disease. The 7-month-old male patient presented with severe metabolic acidosis and elevated liver enzymes. His condition was similar to fatty acid oxidation defect. He was taken to the hospital on the previous day with complaints of poor sucking and difficulty breathing. Treatment of upper respiratory tract infection was provided and then he returned to his home. He was cyanotic in bed after 12 hours. The patient, who was taken to the hospital unconscious and not fed for 12 hours, was not given any food orally in the first health center. Until laboratory tests are done, only iv electrolyte and a fluid containing dextrose were given. When the laboratory results were found to be significantly pathological, he was urgently referred to our hospital 4 hours after the admission. The content of the iv treatment applied at the time of referral was not clearly written. Low electrolytes, uric acid, liver enzymes, urea and creatinine elevation were detected at an outer center. Ketosis, lactic acidosis and dibasic aciduria were detected in urine organic acid analysis. He was diagnosed with Kwashiorkor and refeeding syndrome according to the clinical and laboratory findings. His complaints improved with appropriate treatment.
Keywords: Kwashiorkor; Malnutrition; lactic acidosis.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Severe nutritional deficiencies in toddlers resulting from health food milk alternatives.Pediatrics. 2001 Apr;107(4):E46. doi: 10.1542/peds.107.4.e46. Pediatrics. 2001. PMID: 11335767
-
'Refeeding syndrome' in a Kuwaiti child: clinical diagnosis and management.Med Princ Pract. 2010;19(3):240-3. doi: 10.1159/000285303. Epub 2010 Mar 29. Med Princ Pract. 2010. PMID: 20357512
-
Refeeding syndrome as an unusual cause of anion gap metabolic acidosis.Mil Med. 2012 Nov;177(11):1393-5. doi: 10.7205/milmed-d-11-00432. Mil Med. 2012. PMID: 23198519
-
Severe Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis Resulting from Combined Chronic Acetaminophen Toxicity and Starvation Ketosis: A Case Report and Literature Review.Am J Case Rep. 2022 Jan 17;23:e934410. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.934410. Am J Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35034948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenformin-induced lactic acidosis: a forgotten adverse drug reaction.Ann Pharmacother. 1993 Oct;27(10):1183-7. doi: 10.1177/106002809302701004. Ann Pharmacother. 1993. PMID: 8251683 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources