Rhamnolipids as Green Stabilizers of nZVI and Application in the Removal of Nitrate From Simulated Groundwater
- PMID: 35519607
- PMCID: PMC9062033
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.794460
Rhamnolipids as Green Stabilizers of nZVI and Application in the Removal of Nitrate From Simulated Groundwater
Abstract
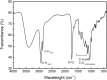
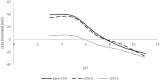
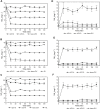
Environmental contamination caused by inorganic compounds is a major problem affecting soils and surface water. Most remediation techniques are costly and generally lead to incomplete removal and production of secondary waste. Nanotechnology, in this scenario with the zero-valent iron nanoparticle, represents a new generation of environmental remediation technologies. It is non-toxic, abundant, cheap, easy to produce, and its production process is simple. However, in order to decrease the aggregation tendency, the zero-iron nanoparticle is frequently coated with chemical surfactants synthesized from petrochemical sources, which are persistent or partially biodegradable. Biosurfactants (rhamnolipids), extracellular compounds produced by microorganisms from hydrophilic and hydrophobic substrates can replace synthetic surfactants. This study investigated the efficiency of a rhamnolipid biosurfactant on the aggregation of nanoscale zer-valent iron (nZVI) and its efficiency in reducing nitrate in simulated groundwater at pH 4.0. Two methods were tested: 1) adding the rhamnolipid during chemical synthesis and 2) adding the rhamnolipid after chemical synthesis of nZVI. Scanning electron microscopy field emission, X-ray diffractometry, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, Dynamic Light Scattering, and zeta potential measurements were used to characterize bare nZVI and rhamnolipid-coated nZVI. The effects of the type of nZVI and initial NO3 concentration were examined. Nanoscale zer-valent iron with the addition of the rhamnolipid after synthesis achieved the best removal rate of nitrate (about 78%), with an initial nitrate concentration of 25 mg L-1. The results suggest that nZVI functionalized with rhamnolipids is a promising strategy for the in situ remediations of groundwater contaminated by NO3, heavy metal, and inorganic carbon.
Keywords: NZVI; groundwater; nitrate removal; rhamnolipids; stabilizer.
Copyright © 2022 Moura, Salazar-Bryam, Piazza, Carvalho dos Santos, Jafelicci, Marques and Contiero.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Enhanced nitrate-nitrogen removal by modified attapulgite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron treating simulated groundwater.J Environ Manage. 2018 May 1;213:151-158. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.02.073. Epub 2018 Feb 26. J Environ Manage. 2018. PMID: 29494931
-
Rhamnolipid biosurfactant and soy protein act as effective stabilizers in the aggregation and transport of palladium-doped zerovalent iron nanoparticles in saturated porous media.Environ Sci Technol. 2013;47(23):13355-64. doi: 10.1021/es402619v. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Environ Sci Technol. 2013. PMID: 24237158
-
Removal of nitrate from groundwater by nano-scale zero-valent iron injection pulses in continuous-flow packed soil columns.Sci Total Environ. 2022 Mar 1;810:152300. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152300. Epub 2021 Dec 10. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 34896509
-
Integration of nanoscale zero-valent iron and functional anaerobic bacteria for groundwater remediation: A review.Environ Int. 2019 Mar;124:265-277. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.01.030. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Environ Int. 2019. PMID: 30660027 Review.
-
An overview of preparation and applications of stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles for soil and groundwater remediation.Water Res. 2016 Sep 1;100:245-266. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.05.019. Epub 2016 May 10. Water Res. 2016. PMID: 27206054 Review.
Cited by
-
Nano-Restoration for Sustaining Soil Fertility: A Pictorial and Diagrammatic Review Article.Plants (Basel). 2022 Sep 14;11(18):2392. doi: 10.3390/plants11182392. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36145792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rhamnolipid-Modified PHB-Ectoine Nanoparticles for Multifunctional Skin Protection Against UVB, Irritation, and Bacteria.ACS Omega. 2025 Mar 17;10(12):12200-12213. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c10583. eCollection 2025 Apr 1. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40191376 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arancibia-Miranda N., Baltazar S. E., García A., Muñoz-Lira D., Sepúlveda P., Rubio M. A., et al. (2016). Nanoscale Zer Valent Supported by Zeolite and Montmorillonite: Template Effect of the Removal of Lead Ion from an Aqueous Solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 301, 371–380. 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.09.007 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Basnet M., Ghoshal S., Tufenkji N. (2013). Rhamnolipid Biosurfactant and Soy Protein Act as Effective Stabilizers in the Aggregation and Transport of Palladium-Doped Zerovalent Iron Nanoparticles in Saturated Porous Media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47 (23), 13355–13364. 10.1021/es402619v - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

