Indoor Pool Game and Substance Abuse as Trajectories to Students' Academic Procrastination: The Mediation Role of Self-Regulation
- PMID: 35519639
- PMCID: PMC9062778
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.835371
Indoor Pool Game and Substance Abuse as Trajectories to Students' Academic Procrastination: The Mediation Role of Self-Regulation
Abstract
Background: Over the last decade, indoor pool games (IPGs) and substance abuse (SA) became a remarkable emerging addictive behavior among adolescent university students. With the failure of educational quality and retention of learners, boomerangs around the university local environment in line with the students' learning culture were not considered in many countries including Ethiopia. Thus, this study aimed to examine the trajectory and contribution of an IPG and SA to students' academic procrastination (AP) as determinants of quality education.
Methods: A sequential explanatory mixed-methods design was employed. Self-reporting questionnaires, interview guides, and an observation checklist were used to collect data. All self-reporting items were adapted from previous scales. By using simple random sampling techniques, 237 undergraduate university students were selected for obtaining the quantitative data, and using purposive sampling, 12 interviewees were selected to collect the qualitative data. The SPSS AMOS version 25 was used to compute the multiple mediation path analysis. The Hayes PROCESS macro model was used. Furthermore, the thematic content analysis method was employed for the qualitative data.
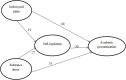
Results: A direct path analysis was established between IPG, SA, and AP. The path analysis model indicated that IPG did not significantly predict AP. Moreover, SA significantly predicted AP. In addition, SR had a partial mediating effect on the relationship between IPG, SA, and AP.
Conclusion: The study concluded that IPG and substances available around the university local environment found trajectories to students' AP, which in turn affects the quality of education.
Keywords: academic procrastination; indoor pool game; mediation; substance abuse; university students.
Copyright © 2022 Gita, Koya and Worku.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abbott M. (2017). The Epidemiology and Impact of Gambling Disorder and other Gambling-Related Harm. WHO Forum on Alcohol, Drugs and Addictive Behaviors Enhancing Public Health Actions through Partnerships and Collaboration 26-28 June 2017. Geneva: WHO. - PubMed
-
- AbdiZarrin S., Gracia E., Paixão M. P. (2020). Prediction of academic procrastination by fear of failure and self-regulation. Educ. Sci. Theory Pract. 20 34–43. 10.12738/jestp.2020.3.003 - DOI
-
- Ahmadi S., Toulabi S., Ilanloo H. (2020). The relationship between tendency to substance abuse and resilience and academic procrastination in secondary school students. J. Arak Univ. Med. Sci. 23 108–117. 10.32598/JAMS.23.1.5972.1 - DOI
-
- Akinci T. (2021). Determination of predictive relationships between problematic smartphone use, self-regulation, academic procrastination, and academic stress through modeling. Int. J. Progress. Educ. 17 35–53. 10.29329/ijpe.2020.329.3 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials