Cyclohexamer [-(d-Phe-azaPhe-Ala)2-]: good candidate to formulate supramolecular organogels
- PMID: 35519698
- PMCID: PMC9058333
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra07775e
Cyclohexamer [-(d-Phe-azaPhe-Ala)2-]: good candidate to formulate supramolecular organogels
Abstract
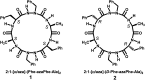
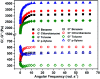
Molecular self-assembly is a fascinating process which has become an area of great interest in supramolecular chemistry, as it leads in certain cases to molecular gels. Organogels formulated from low molecular weight compounds (LMWOGs) have attracted much interest in the past decades due to their applications as new soft materials. Herein, we report on the ability of the cyclic pseudopeptide cyclo-[-(d-Phe-azaPhe-Ala)2-] (2) to self-assemble in some aromatic solvents and to form organogels driven by non-covalent forces, mainly hydrogen bonding and π-stacking interactions. Comprehensive FTIR and NMR studies emphasized that this cyclic aza-peptide adopts a β-turn conformation at low concentration in toluene, while an equilibrium between the monomeric states (intramolecular forces) and the supramolecular structures (intra- and intermolecular forces) is established at high concentration (gel state). Rheological investigations of the organogels highlight the dependence of their stiffness (up to ∼4 kPa) and sol/gel transition temperatures (up to 100 °C) as a function of the solvent and concentration of gelator used. The formulation of fibrous structures confirmed the phenomenon of self-assembly. Finally, we found that cyclo-[-(d-Phe-azaPhe-Ala)2-] is an effective organogelator for application in phase selective gelation (PSG) of organic solvents from aqueous/organic mixtures with recovery percents up to 96%.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Solvent Effects on Gelation Behavior of the Organogelator Based on L-Phenylalanine Dihydrazide Derivatives.Materials (Basel). 2019 Jun 12;12(12):1890. doi: 10.3390/ma12121890. Materials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31212767 Free PMC article.
-
Birefringent physical gels of N-(4-n-alkyloxybenzoyl)-L-alanine amphiphiles in organic solvents: the role of hydrogen-bonding.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2010 Apr 1;344(1):10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2009.12.003. Epub 2009 Dec 6. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2010. PMID: 20097349
-
The beta-turn scaffold of tripeptide containing an azaphenylalanine residue.Biophys Chem. 2007 Jan;125(1):117-26. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2006.05.028. Epub 2006 Aug 4. Biophys Chem. 2007. PMID: 16890344
-
Phenylalanine and derivatives as versatile low-molecular-weight gelators: design, structure and tailored function.Biomater Sci. 2017 Dec 19;6(1):38-59. doi: 10.1039/c7bm00882a. Biomater Sci. 2017. PMID: 29164186 Review.
-
Advances in the Supramolecular Chemistry of Tetracoordinate Boron-Containing Organic Molecules into Organogels and Mesogens.Front Chem. 2021 Sep 7;9:708854. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.708854. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 34557473 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A lysine-based 2:1-[α/aza]-pseudopeptide series used as additives in polymeric membranes for CO2 capture: synthesis, structural studies, and application.RSC Adv. 2023 Mar 29;13(15):10051-10067. doi: 10.1039/d3ra00409k. eCollection 2023 Mar 27. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37006376 Free PMC article.
-
Stereochemical Behavior of Pyrrolo-Pyrazole Peptidomimetics Promoting Phase-Selective Supramolecular Organogels.Gels. 2024 Apr 14;10(4):263. doi: 10.3390/gels10040263. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38667682 Free PMC article.
-
Production and Characterization of Exopolysaccharide From Newly Isolated Marine Probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum EI6 With in vitro Wound Healing Activity.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 13;13:903363. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.903363. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35668753 Free PMC article.
-
Considerable Production of Ulvan from Ulva lactuca with Special Emphasis on Its Antimicrobial and Anti-fouling Properties.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2022 Jul;194(7):3097-3118. doi: 10.1007/s12010-022-03867-y. Epub 2022 Mar 26. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35347670 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

