Noble metal sensitized invasive porous bioelectrodes: advanced medical device for enhanced neuronal activity and chronic alcohol treatment
- PMID: 35519706
- PMCID: PMC9058419
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra07922g
Noble metal sensitized invasive porous bioelectrodes: advanced medical device for enhanced neuronal activity and chronic alcohol treatment
Abstract
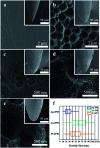
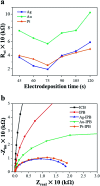
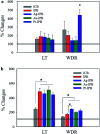
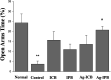
Invasive bioelectrodes are widely used as an effective treatment for several acute and chronic diseases. In earlier work using high surface area invasive porous bioelectrodes evaluated in an animal model of alcoholism withdrawal, we demonstrated significantly improved electrophysiological and behavioral responses. In this study, we further modify the surface of these invasive porous bioelectrodes with noble metal (Ag, Au, Pt) nanoparticles. Compared to both conventional and porous bioelectrodes, noble metal sensitized invasive porous bioelectrodes show markedly increased low threshold (LT) and wide dynamic range (WDR) neuronal activity. In particular, Pt-sensitized invasive porous bioelectrodes show the highest WDR neuronal activity only upon insertion. In addition, Ag-sensitized invasive porous bioelectrodes, whose surface area is about 37 times greater than that of conventional bioelectrodes, show improved electrochemical properties with higher LT and WDR neuronal activity when stimulated. In an animal model of chronic alcoholism, using normal and alcohol-treated Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats evaluated with the elevated plus maze (EPM) test, the Ag-sensitized invasive porous bioelectrodes show about 20% higher open arms time. These results suggest that these noble metal-sensitized invasive bioelectrodes may offer improved therapeutic outcomes for the treatment of chronic alcoholism, and given these enhanced electrophysiological properties, for other conditions as well.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Decoration of Micro-/Nanoscale Noble Metal Particles on 3D Porous Nickel Using Electrodeposition Technique as Electrocatalyst for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction in Alkaline Electrolyte.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015 Jul 29;7(29):15716-25. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b00679. Epub 2015 Jul 14. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015. PMID: 26125300
-
Effects of nanostructuration on the electrochemical performance of metallic bioelectrodes.Nanoscale. 2022 Feb 24;14(8):3179-3190. doi: 10.1039/d1nr06280h. Nanoscale. 2022. PMID: 35142756
-
Electrochemical Co-deposition of Polydopamine/Hyaluronic Acid for Anti-biofouling Bioelectrodes.Front Chem. 2019 Apr 30;7:262. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00262. eCollection 2019. Front Chem. 2019. PMID: 31114782 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in fuel cell reaction electrocatalysis based on porous noble metal nanocatalysts.Dalton Trans. 2022 May 24;51(20):7763-7774. doi: 10.1039/d2dt00841f. Dalton Trans. 2022. PMID: 35508098 Review.
-
Implantable bioelectrodes: challenges, strategies, and future directions.Biomater Sci. 2024 Jan 16;12(2):270-287. doi: 10.1039/d3bm01204b. Biomater Sci. 2024. PMID: 38175154 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

