Enhanced reductive removal of ciprofloxacin in pharmaceutical wastewater using biogenic palladium nanoparticles by bubbling H2
- PMID: 35519754
- PMCID: PMC9055312
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra03783d
Enhanced reductive removal of ciprofloxacin in pharmaceutical wastewater using biogenic palladium nanoparticles by bubbling H2
Abstract
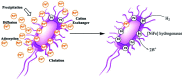
To treat waste with waste and efficiently remove the organic pollutant, waste palladiums(ii) were adsorbed and reduced on microorganism surface to catalyze the reductive removal of ciprofloxacin in pharmaceutical wastewater. By optimizing conditions such as pH and temperature, the amount of biogenic palladium adsorbed and reduced on E. coli reached 139.48 mg g-1 (Pd/microorganisms). Moreover, most of the Pd(ii) was reduced to nanometer-sized Pd(0) as characterized by TEM and SEM with EDXA. Using the obtained biogenic palladium, the reductive removal of ciprofloxacin is up to 87.70% at 25 °C, 3.03 folds of that achieved in the absence of H2. The results show that waste E. coli microorganisms can efficiently adsorb and remove waste Pd(ii) and produce Bio-Pd nanoparticle catalysts in the presence of H2. This biogenic palladium presents high catalytic activity and great advantages in the reductive degradation of ciprofloxacin. Our method can also be applied to other waste metal ions to prepare the biogenic metals, facilitate their recovery and reuse in degrading organic pollutants in wastewater to achieve "treating waste using waste".
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Electrochemically assisted production of biogenic palladium nanoparticles for the catalytic removal of micropollutants in wastewater treatment plants effluent.J Environ Sci (China). 2023 Jun;128:203-212. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2022.08.018. Epub 2022 Aug 27. J Environ Sci (China). 2023. PMID: 36801035
-
Biogenic platinum and palladium nanoparticles as new catalysts for the removal of pharmaceutical compounds.Water Res. 2017 Jan 1;108:160-168. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.10.071. Epub 2016 Oct 28. Water Res. 2017. PMID: 27817891
-
Doping of biogenic Pd catalysts with Au enables dechlorination of diclofenac at environmental conditions.Water Res. 2012 May 15;46(8):2718-26. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.02.036. Epub 2012 Feb 24. Water Res. 2012. PMID: 22406286
-
Upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor--a review.Indian J Environ Health. 2001 Apr;43(2):1-82. Indian J Environ Health. 2001. PMID: 12397675 Review.
-
Biotechnological synthesis of Pd-based nanoparticle catalysts.Nanoscale Adv. 2021 Dec 21;4(3):654-679. doi: 10.1039/d1na00686j. eCollection 2022 Feb 1. Nanoscale Adv. 2021. PMID: 35224444 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extremophilic Exopolysaccharides: Biotechnologies and Wastewater Remediation.Front Microbiol. 2021 Aug 19;12:721365. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.721365. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34489911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Salts and Other Contaminants on Ciprofloxacin Removal Efficiency of Green Synthesized Copper Nanoparticles.Vet Sci. 2024 Apr 16;11(4):179. doi: 10.3390/vetsci11040179. Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38668446 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Potential of Endophytic Microorganisms and Nanoparticles for Enhanced Water Remediation.Molecules. 2024 Jun 16;29(12):2858. doi: 10.3390/molecules29122858. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38930923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced photocatalytic performance of rhodamine B and enrofloxacin by Pt loaded Bi4V2O11: boosted separation of charge carriers, additional superoxide radical production, and the photocatalytic mechanism.RSC Adv. 2021 Mar 5;11(16):9746-9755. doi: 10.1039/d1ra00055a. eCollection 2021 Mar 1. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35423437 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sattayarut V. Chanthad C. Khemthong P. Kuboon S. Wanchaem T. Phonyiem M. Obata M. Fujishige M. Takeuchi K. Wongwiriyapan W. Khanchaitit P. Endo M. Preparation and electrochemical performance of nitrogen-enriched activated carbon derived from silkworm pupae waste. RSC Adv. 2019;9:9878–9886. doi: 10.1039/C9RA01090D. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Noah N. F. M. Othman N. Jusoh N. Highly selective transport of palladium from electroplating wastewater using emulsion liquid membrane process. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016;64:134–141. doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2016.03.047. - DOI
-
- Huang D. Li B. Ou J. Xue W. Li J. Li Z. Li T. Chen S. Deng R. Guo X. Megamerger of biosorbents and catalytic technologies for the removal of heavy metals from wastewater: preparation, final disposal, mechanism and influencing factors. J. Environ. Manage. 2020;261:109879. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109879. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

