Amorphous mesostructured zirconia with high (hydro)thermal stability
- PMID: 35519781
- PMCID: PMC9055362
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra04824k
Amorphous mesostructured zirconia with high (hydro)thermal stability
Abstract
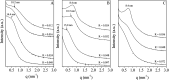
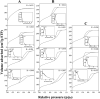
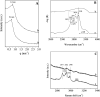
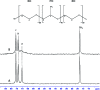
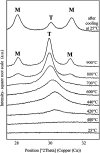
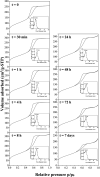
Here, combining the evaporation-induced self-assembly (EISA) method and the liquid crystal templating pathway, mesostructured amorphous zirconium oxides have been prepared by a soft templating method without addition of any heteroelement to stabilize the mesopore framework. The recovered materials have been characterized by SAXS measurements, nitrogen adsorption-desorption analysis and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The obtained mesostructured zirconia exhibits a high thermal stability. An in situ XRD study performed as a function of temperature shows that the amorphous ZrO2, obtained after removal of the pore templating agent (pluronic P123), begins to crystallize in air from 420 °C. Amorphous mesostructured ZrO2 also presents a high hydrothermal stability; these materials are not degraded after 72 hours in boiling water.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Inoue Y. Yamazaki H. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1987;60:891. doi: 10.1246/bcsj.60.891. - DOI
-
- Jaenicke S. Chuah G. K. Raju V. Nie Y. T. Catal. Surv. Asia. 2008;12:153. doi: 10.1007/s10563-008-9048-2. - DOI
-
- Srinivasan R. and Davis B. H., in Materials Synthesis and Characterization, ed. D. L. Perry, Springer Science+Business Media, New York, 1997, pp. 147–188
-
- Lin C. Zhang C. Lin J. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2007;111:3300. doi: 10.1021/jp066615l. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

