Cu(ii) immobilized on Fe3O4@HNTs-tetrazole (CFHT) nanocomposite: synthesis, characterization, investigation of its catalytic role for the 1,3 dipolar cycloaddition reaction, and antibacterial activity
- PMID: 35519782
- PMCID: PMC9055433
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra04772d
Cu(ii) immobilized on Fe3O4@HNTs-tetrazole (CFHT) nanocomposite: synthesis, characterization, investigation of its catalytic role for the 1,3 dipolar cycloaddition reaction, and antibacterial activity
Abstract
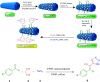
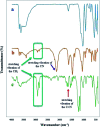
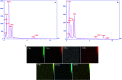
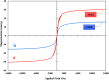
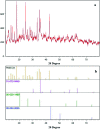
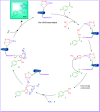
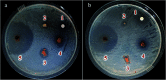
In the present study, Cu(ii) immobilized on an Fe3O4@HNTs-tetrazole (CFHT) nanocomposite was designed and prepared. For this, halloysite nanotubes (HNTs) as natural mesoporous substances were modified during several chemical reactions. The synthesis of the CFHT nanocomposite was investigated step by step with the required physicochemical techniques such as FT-IR, EDX, SEM, TEM, XRD, VSM, TGA and CHNS analyses. After ensuring that the nanocomposite was successfully prepared, its catalytic application in the synthesis of the 5-substituted 1H-tetrazole derivatives via multicomponent reactions (MCRs) between aromatic aldehydes, malononitrile, and sodium azide was assessed. According to the experimental results, the prepared nanocomposite exhibited excellent capability for conducting this MCR reaction. All desired products were obtained in a short reaction time (30-40 min) with high productivity (90-97%) and without a complicated workup procedure. Furthermore, the magnetic property of the synthesized heterogeneous nanocomposite empowers it to be recovered and reused in five times successive reactions without any significant reduction in reaction efficiency. Moreover, the remarkable antibacterial activity of the nanocomposite against Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) was evaluated by agar diffusion and plate-count methods. The zones of inhibition were around 16 and 20 mm for E. coli and S. aureus bacteria, respectively. Also, colony analysis confirms the killing of bacteria by using the CFHT nanocomposite.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Assessment of catalytic and antibacterial activity of biocompatible agar supported ZnS/CuFe2O4 magnetic nanotubes.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 16;12(1):4503. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-08318-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35297399 Free PMC article.
-
Superparamagnetic Poly(aniline-co-m-phenylenediamine)@Fe3O4 Nanocomposite as an Efficient Heterogeneous Catalyst for the Synthesis of 1H-pyrazolo[1,2-a]pyridazine-5,8-diones & 1H-pyrazolo[1,2-b]phthalazine-5, 10-diones Derivatives.Curr Org Synth. 2022 Mar 3;19(2):246-266. doi: 10.2174/1570179418666211104143736. Curr Org Synth. 2022. PMID: 34736384
-
Guanidinylated SBA-15/Fe3O4 mesoporous nanocomposite as an efficient catalyst for the synthesis of pyranopyrazole derivatives.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 6;11(1):19852. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99120-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34615925 Free PMC article.
-
The anchoring of a Cu(ii)-salophen complex on magnetic mesoporous cellulose nanofibers: green synthesis and an investigation of its catalytic role in tetrazole reactions through a facile one-pot route.RSC Adv. 2021 May 27;11(31):19203-19220. doi: 10.1039/d1ra01913a. eCollection 2021 May 24. RSC Adv. 2021. Retraction in: RSC Adv. 2024 Jan 5;14(3):1672. doi: 10.1039/d3ra90132g. PMID: 35478649 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
New magnetic nanocomposite Fe3O4@Saponin/Cu(II) as an effective recyclable catalyst for the synthesis of aminoalkylnaphthols via Betti reaction.Steroids. 2023 Mar;191:109170. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2022.109170. Epub 2022 Dec 29. Steroids. 2023. PMID: 36587779 Review.
Cited by
-
Design and characterization of an urea-bridged PMO supporting Cu(II) nanoparticles as highly efficient heterogeneous catalyst for synthesis of tetrazole derivatives.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 28;12(1):18139. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22905-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36307538 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of (E)-2-(1H-tetrazole-5-yl)-3-phenylacrylenenitrile derivatives catalyzed by new ZnO nanoparticles embedded in a thermally stable magnetic periodic mesoporous organosilica under green conditions.Sci Rep. 2022 Jun 24;12(1):10723. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-13011-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35750767 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of Cu(OH)2 nanowires modified by Fe3O4@SiO2 nanocomposite via green and innovative method with antibacterial activity and investigation of magnetic behaviours.R Soc Open Sci. 2022 Jun 1;9(6):212025. doi: 10.1098/rsos.212025. eCollection 2022 Jun. R Soc Open Sci. 2022. PMID: 35706673 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis, and characterization of novel eco-friendly chitosan-AgIO3 bionanocomposite and study its antibacterial activity.Sci Rep. 2022 Jun 21;12(1):10491. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-14501-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35729281 Free PMC article.
-
Periodic mesoporous organosilica functionalized with p-aminobenzenesulfonic acid: an efficient solid acid catalyst for one-pot synthesis of 5-substituted 1H-tetrazoles under eco-friendly conditions.Nanoscale Adv. 2025 May 19;7(15):4691-4709. doi: 10.1039/d5na00224a. eCollection 2025 Jul 22. Nanoscale Adv. 2025. PMID: 40575618 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barrientos-Ramírez S. de Oca-Ramírez G. M. Ramos-Fernández E. Sepúlveda-Escribano A. Pastor-Blas M. González-Montiel A. Appl. Catal., A. 2011;406:22–33. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2011.08.003. - DOI
-
- Hillier S. Brydson R. Delbos E. Fraser T. Gray N. Pendlowski H. Phillips I. Robertson J. Wilson I. Clay Miner. 2016;51:325–350. doi: 10.1180/claymin.2016.051.3.11. - DOI
-
- Hajizadeh Z. Maleki A. Mol. Catal. 2018;460:87–93. doi: 10.1016/j.mcat.2018.09.018. - DOI
-
- Rawtani D. Agrawal Y. K. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2012;30:282–295.
-
- Hajizadeh Z. Valadi K. Taheri-Ledari R. Maleki A. ChemistrySelect. 2020;5:2441–2448. doi: 10.1002/slct.201904672. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

