Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Predictor of Disease Severity and Mortality in Coronavirus Disease 2019: Prospective Study From Central India
- PMID: 35519791
- PMCID: PMC9064266
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.23696
Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Predictor of Disease Severity and Mortality in Coronavirus Disease 2019: Prospective Study From Central India
Abstract
Background: Clinical presentation of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) varies from an asymptomatic state to severe disease characterized by acute respiratory distress syndrome, respiratory failure, thrombosis, and multi-organ dysfunction syndrome. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) has been reviewed as one of the laboratory factors that have been proposed to predict the severity of disease and mortality in COVID-19 pandemic.
Aim and objectives: To evaluate the association between NLR and the disease severity and mortality in COVID-19.
Materials and methods: After approval from Institutional Ethics Committee, this prospective cohort study was carried out in a tertiary-care teaching medical institute of Central India. COVID-19 patients of the age group 18 years and above admitted during the study period were included. Cases were categorized into four groups as asymptomatic (Group A), mild (Group B), moderate (Group C), and severe (Group D) based on clinical symptoms, respiratory rate, oxygen saturation, and chest imaging. NLR was calculated by doing a complete blood count at the time of hospitalization by the Mindray BC-6000 auto hematology analyzer. The outcome of the disease was classified as recovery and death during hospitalization. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to assess the ability of NLR at admission to predict severe COVID-19 or mortality. Ordinal regression analysis was used to assess the impact of NLR on disease severity and mortality.
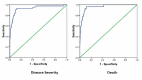
Results: Mean NLR was significantly higher in the severe COVID-19 group as compared to the mild/moderate group and in deceased as compared to discharged cases. ROC curve analysis revealed NLR to be an excellent predictor of disease severity as well as a prognostic parameter for risk of death. NLR was found to be a significant independent positive predictor for contracting the severe disease (Odd's ratio 1.396, 95% CI=1.112-1.753, p=0.004) and mortality (Odd's ratio 1.276, 95% CI=1.085-1.499, p=0.003).
Conclusion: High NLR was significantly associated with the disease severity and mortality in COVID-19.
Keywords: covid-19; cytokine storm; mortality; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (nlr); severity.
Copyright © 2022, Rathod et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of vitamin D with the severity of disease and mortality in COVID-19: Prospective study in central India.Ann Afr Med. 2023 Jan-Mar;22(1):117-123. doi: 10.4103/aam.aam_21_22. Ann Afr Med. 2023. PMID: 36695233 Free PMC article.
-
Routine hematology parameters in COVID-19: A predictor of disease severity and mortality.J Family Med Prim Care. 2022 Jul;11(7):3423-3429. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_2453_21. Epub 2022 Jul 22. J Family Med Prim Care. 2022. PMID: 36387722 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Their Role as Predictors of Disease Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19).J Lab Physicians. 2021 Mar;13(1):58-63. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1723057. Epub 2021 Feb 22. J Lab Physicians. 2021. PMID: 34103879 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio on admission to predict the severity and mortality of COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis.Am J Emerg Med. 2021 Apr;42:60-69. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2021.01.006. Epub 2021 Jan 9. Am J Emerg Med. 2021. PMID: 33453617 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Risk Stratification and Prognostication of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Aug 1;10(8):1233. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10081233. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36016121 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Elevated Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio on Adverse Outcomes in Patients With Myocardial Infarction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2024 Jun 4;16(6):e61647. doi: 10.7759/cureus.61647. eCollection 2024 Jun. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38966451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monitoring the Efficacy of High-Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy in Patients with Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure in the General Respiratory Ward: A Prospective Observational Study.Biomedicines. 2023 Nov 16;11(11):3067. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11113067. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38002067 Free PMC article.
-
Coagulation parameters abnormalities and their relation to clinical outcomes in hospitalized and severe COVID-19 patients: prospective study.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 1;12(1):13155. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16915-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35915103 Free PMC article.
-
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) to determine cut-off points of clinical and biomolecular markers to discriminate mortality in severe COVID-19 living at high altitude.BMC Pulm Med. 2023 Oct 18;23(1):393. doi: 10.1186/s12890-023-02691-2. BMC Pulm Med. 2023. PMID: 37848858 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Associated with All-Cause 30-Day Mortality in Indonesian Inpatient COVID-19 Patients at Cipto Mangunkusumo National General Hospital.J Clin Med. 2024 May 20;13(10):2998. doi: 10.3390/jcm13102998. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38792539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organisation. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. [ May; 2022 ];https://covid19.who.int 2022
-
- The systemic inflammation-based neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: experience in patients with cancer. Guthrie GJ, Charles KA, Roxburgh CS, Horgan PG, McMillan DC, Clarke SJ. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2013;88:218–230. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
