Effective resource management using machine learning in medicine: an applied example
- PMID: 35519832
- PMCID: PMC8936600
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjstel-2017-000289
Effective resource management using machine learning in medicine: an applied example
Abstract
Background: The field of medicine is rapidly becoming digitised, and in the process passively amassing large volumes of healthcare data. Machine learning and data analytics are advancing rapidly, but these have been slow to be taken up in the day-to-day delivery of healthcare. We present an application of machine learning to optimise a laboratory testing programme as an example of benefiting from these tools.
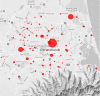
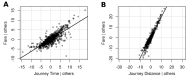
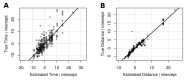
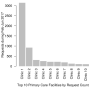
Methods: Canterbury District Health Board has recently implemented a system for urgent lab sample processing in the community, reducing unnecessary emergency presentations to hospital. Samples are transported from primary care facilities to a central laboratory. To improve the efficiency of this service, our team built a prototype transport scheduling platform using machine learning techniques and simulated the efficiency and cost impact of the platform using historical data.
Results: Our simulation demonstrated procedural efficiency and potential for annual savings between 5% and 14% from implementing a real-time lab sample transport scheduling platform. Advantages included providing a forward job list to the laboratory, an expected time to result and a streamlined transport request process.
Conclusion: There are a range of opportunities in healthcare to use large datasets for improved delivery of care. We have described an applied example of using machine learning techniques to improve the efficiency of community patient lab sample processing at scale. This is with a view to demonstrating practical avenues for collaboration between clinicians and machine learning engineers.
Keywords: clinical informatics; healthcare resource utilization; inefficiency in health; primary care; resource management big data.
© Article author(s) (or their employer(s) unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2019. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: AW and JW are co-founders of the software company Isogonal.
Figures
References
-
- Lehtonen H, Lukkarinen T, Kämäräinen V, et al. Improving emergency department capacity efficiency. Signa Vitae - A Journal In Intensive Care And Emergency Medicine 2016;12:52–7. 10.22514/SV121.102016.9 - DOI
-
- Hastie T, Tibshirani R, Friedman J. The elements of statistical learning: data mining, inference, and prediction. Second Edn. Springer: Springer Series in Statistics, 2017.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
