The selection of highly specific and selective aptamers using modified SELEX and their use in process analytical techniques for Lucentis bioproduction
- PMID: 35520059
- PMCID: PMC9055848
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra03542d
The selection of highly specific and selective aptamers using modified SELEX and their use in process analytical techniques for Lucentis bioproduction
Abstract
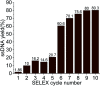
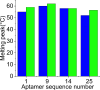
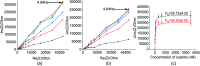
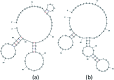
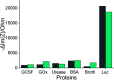
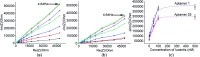
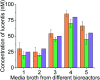
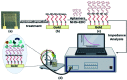
Aptamers for Lucentis were selected using 10 rounds of a modified and highly stringent SELEX process. Affinity column chromatography was used for the binding, partitioning, and elution steps, and the regeneration of ssDNA was performed via asymmetric PCR in the SELEX process. The interaction of aptamers with Lucentis was studied by means of the HADDOCK web server docking program. In addition, the secondary structures of aptamers were interrogated using the mfold web server to check common regions responsible for better affinity towards Lucentis. The two best aptamers for Lucentis (aptamers 1 and 25) were found to have dissociation constant (K d) values between 23 and 35 nM by means of thermofluorimetric and non-faradaic impedance spectroscopy (NFIS) analysis. The low dissociation constants in the nanomolar range showed the high specificities of the aptamers for Lucentis. Selectivity tests were also performed using both aptamers with different proteins in which negligible responses were obtained from interfering proteins with respect to Lucentis. Although neither of the two aptamers showed prominent responses to the interfering proteins, slightly better selectivity was shown by aptamer 1. The same aptamers were tested for their application in the detection of Lucentis in spiked and real media broth samples. For this detection test, interdigitated (IDT) gold electrodes on a glass substrate were fabricated using standard photolithography and thermal deposition techniques. NFIS measurements were used for the label-free detection of Lucentis in samples. The linear ranges of detection for aptamers 1 and 25 were found to be 22-100 nM and 40-100 nM, respectively. The LODs for aptamers 1 and 25 were calculated to be 22 nM and 40 nM, respectively, which were significantly better than the values from a HPLC-based detection method (about 240 nM). The real sample analysis results were cross-checked via a standard HPLC method, and better correlation was found between the HPLC and aptamer 1 results than the aptamer 25 results; hence, aptamer 1 can be further analyzed and tested for use in affinity column chromatography and detection-kit/chip-based PAT for Lucentis bioproduction.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
An improved SELEX technique for selection of DNA aptamers binding to M-type 11 of Streptococcus pyogenes.Methods. 2016 Mar 15;97:51-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.12.005. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Methods. 2016. PMID: 26678795
-
DNA aptamers selection and characterization for development of label-free impedimetric aptasensor for neurotoxin anatoxin-a.Biosens Bioelectron. 2015 Jun 15;68:295-302. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Jan 2. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015. PMID: 25594161
-
Staggered Target SELEX, a novel approach to isolate non-cross-reactive aptamer for detection of SEA by apta-qPCR.J Biotechnol. 2018 Nov 20;286:45-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2018.09.006. Epub 2018 Sep 18. J Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30236483
-
In silico approach for Post-SELEX DNA aptamers: A mini-review.J Mol Graph Model. 2021 Jun;105:107872. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2021.107872. Epub 2021 Mar 2. J Mol Graph Model. 2021. PMID: 33765525 Review.
-
Development of Cell-Specific Aptamers: Recent Advances and Insight into the Selection Procedures.Molecules. 2017 Nov 27;22(12):2070. doi: 10.3390/molecules22122070. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29186905 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aptamer Screening: Current Methods and Future Trend towards Non-SELEX Approach.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Jul 18;14(7):350. doi: 10.3390/bios14070350. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39056626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perspective-Assessing Electrochemical, Aptamer-Based Sensors for Dynamic Monitoring of Cellular Signaling.ECS Sens Plus. 2023 Dec 1;2(4):042401. doi: 10.1149/2754-2726/ad15a1. Epub 2023 Dec 27. ECS Sens Plus. 2023. PMID: 38152504 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling the Ocular Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Ranibizumab for Improved Understanding and Data Collection Strategies in Ocular Diseases.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025 Jun 2;66(6):20. doi: 10.1167/iovs.66.6.20. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025. PMID: 40478563 Free PMC article.
-
A novel DNA aptamer for Vibrio cholerae O139 detection: a whole-cell SELEX approach.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jun 9;52(1):569. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10677-y. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40488973 No abstract available.
-
Recent Advances in Micro/Nanomaterial-Based Aptamer Selection Strategies.Molecules. 2021 Aug 26;26(17):5187. doi: 10.3390/molecules26175187. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34500620 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sigl R., US Pat., 2016/0297877A1, 2016, vol. 1
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

