Synthesis of benzonaphthofuroquinones and benzoylnaphthindolizinediones by reactions of flavonoids with dichlone under basylous, oxygenous and aqueous conditions: their cytotoxic and apoptotic activities
- PMID: 35520063
- PMCID: PMC9055798
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra06043g
Synthesis of benzonaphthofuroquinones and benzoylnaphthindolizinediones by reactions of flavonoids with dichlone under basylous, oxygenous and aqueous conditions: their cytotoxic and apoptotic activities
Abstract
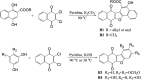
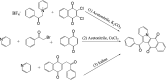
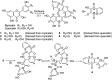
Using flavonoids and dichlone as substrates, benzonaphthofuroquinones (1, 2, 3, 5, 6, novel; 4 new) and benzoylnaphthindolizinediones (7, 8, known; 9, new) were synthesized through common base-catalyzed method and a new method of combining base-catalyzed with O2/H2O exposing. The possible reaction mechanisms may involve the process like isomerization, hydration, oxidation, decomposition and intermolecular condensation. Benzonaphthofuroquinones (2, 3, 4, 5) were found to exhibit potent cytotoxicity against carcinoma cell lines and low toxicity to normal cell lines. The compounds 4 and 5 not only expressed a significant late-stage-apoptosis against human leukemia and melanoma, but also promoted the cleavage of caspase-3 and PARP in human leukemia, which suggested that the late-stage-apoptosis and caspase-3 pathway may be responsible for the cytotoxicities of these benzonaphthofuroquinones. The replacement of the furan ring with pyrrole system in benzoylnaphthindolizinediones (7, 8, 9) resulted in the loss of anticancer activity.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
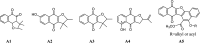
Similar articles
-
Cytotoxic and Apoptotic Effects of Novel Pyrrolo[2,3-d]Pyrimidine Derivatives Containing Urea Moieties on Cancer Cell Lines.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2018;18(9):1303-1312. doi: 10.2174/1871520618666180605082026. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29866023
-
Design, synthesis, and biologic evaluation of novel chrysin derivatives as cytotoxic agents and caspase-3/7 activators.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Jan 22;13:423-433. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S189476. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 30774307 Free PMC article.
-
Cycloartobiloxanthone Induces Human Lung Cancer Cell Apoptosis via Mitochondria-dependent Apoptotic Pathway.In Vivo. 2018 Jan-Feb;32(1):71-78. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11206. In Vivo. 2018. PMID: 29275301 Free PMC article.
-
The anticancer potential of flavonoids isolated from the stem bark of Erythrina suberosa through induction of apoptosis and inhibition of STAT signaling pathway in human leukemia HL-60 cells.Chem Biol Interact. 2013 Sep 25;205(2):128-37. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2013.06.020. Epub 2013 Jul 9. Chem Biol Interact. 2013. PMID: 23850732
-
Considerations on the mechanism of action of artemisinin antimalarials: part 1--the 'carbon radical' and 'heme' hypotheses.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2013 Aug;13(4):217-77. doi: 10.2174/1871526513666131129155708. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2013. PMID: 24304352 Review.
References
-
- Morello A. Pavani M. Garbarino J.-A. Chamy M.-C. Frey C. Mancilla J. Guerrero A. Repetto Y. Ferreira J. Comp. Biochem. Physiol., Part C: Pharmacol., Toxicol. Endocrinol. 1995;112:119–128. - PubMed
-
- Cho H. Park S.-J. Lee K.-I. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2005;26:1829–1832. doi: 10.5012/bkcs.2005.26.11.1829. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

