Importance of the biofilm matrix for the erosion stability of Bacillus subtilis NCIB 3610 biofilms
- PMID: 35520264
- PMCID: PMC9063333
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra01955c
Importance of the biofilm matrix for the erosion stability of Bacillus subtilis NCIB 3610 biofilms
Abstract
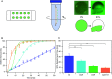
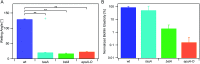
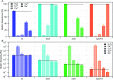
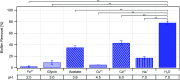
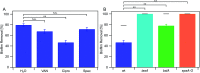
Production and secretion of biomolecules can provide new emergent functionalities to the synthesizing organism. In particular, the secretion of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) by biofilm forming bacteria creates a biofilm matrix that protects the individual bacteria within the biofilm from external stressors such as antibiotics, chemicals and shear flow. Although the main matrix components of biofilms formed by Bacillus subtilis are known, it remains unclear how these matrix components contribute to the erosion stability of B. subtilis biofilms. Here, we combine different biophysical techniques to assess this relation. In particular, we quantify the importance of specific biofilm matrix components on the erosion behavior of biofilms formed by the well-studied Bacillus subtilis NCIB 3610. We find that the absence of biofilm matrix components decreases the erosion stability of NCIB 3610 biofilms in water, largely by abolishing the hydrophobic surface properties of the biofilm and by reducing the biofilm stiffness. However, the erosion resistance of NCIB 3610 biofilms is strongly increased in the presence of metal ions or the antibiotic ciprofloxacin. In the first case, unspecific ionic cross-linking of biofilm components or individual bacteria seems to be responsible for the observed effect, and in the second case there seems to be an unspecific interaction between the antibiotic and the biofilm matrix. Taken together, our results emphasize the importance of the biofilm matrix to reduce biofilm erosion and give insights into how the specific biomolecules interact with certain chemicals to fulfill this task.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Direct Comparison of Physical Properties of Bacillus subtilis NCIB 3610 and B-1 Biofilms.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016 Apr 4;82(8):2424-2432. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03957-15. Print 2016 Apr. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26873313 Free PMC article.
-
Biofilm hydrophobicity in environmental isolates of Bacillus subtilis.Microbiology (Reading). 2021 Sep;167(9). doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001082. Microbiology (Reading). 2021. PMID: 34486975
-
Selected metal ions protect Bacillus subtilis biofilms from erosion.Metallomics. 2014 Aug;6(8):1441-50. doi: 10.1039/c4mt00049h. Metallomics. 2014. PMID: 24770836
-
Biofilm Matrixome: Extracellular Components in Structured Microbial Communities.Trends Microbiol. 2020 Aug;28(8):668-681. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2020.03.016. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Trends Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32663461 Review.
-
The biofilm matrix: multitasking in a shared space.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2023 Feb;21(2):70-86. doi: 10.1038/s41579-022-00791-0. Epub 2022 Sep 20. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36127518 Review.
Cited by
-
Topography quantifications allow for identifying the contribution of parental strains to physical properties of co-cultured biofilms.Biofilm. 2021 Feb 6;3:100044. doi: 10.1016/j.bioflm.2021.100044. eCollection 2021 Dec. Biofilm. 2021. PMID: 33665611 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Metal Cations on the Viscoelastic Properties of Escherichia coli Biofilms.ACS Omega. 2023 Jan 27;8(5):4667-4676. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c06438. eCollection 2023 Feb 7. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 36777596 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabigerol Effect on Streptococcus mutans Biofilms-A Computational Approach to Confocal Image Analysis.Front Microbiol. 2022 Apr 29;13:880993. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.880993. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35572682 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the growth and mechanical properties of Bacillus subtilis biofilms through genetic mutation strategies.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2022 Jun 3;7(3):965-971. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2022.05.005. eCollection 2022 Sep. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35756965 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental challenges in determining the rheological properties of bacterial biofilms.Interface Focus. 2022 Oct 14;12(6):20220032. doi: 10.1098/rsfs.2022.0032. eCollection 2022 Dec 6. Interface Focus. 2022. PMID: 36330324 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

