The Texture of Camel Milk Cheese: Effects of Milk Composition, Coagulants, and Processing Conditions
- PMID: 35520282
- PMCID: PMC9062519
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.868320
The Texture of Camel Milk Cheese: Effects of Milk Composition, Coagulants, and Processing Conditions
Abstract
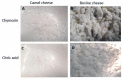
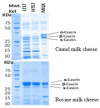
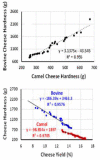
Numerous people in African, Middle Asian, Middle Eastern, and Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries highly value camel milk (CM) as it plays a vital role in their diet. The protein composition of CM as well as the structure of its casein micelles differs significantly from bovine milk (BM). Cheeses made from CM have a weak curd and soft texture compared to those made from BM. This review article presents and discusses the effect of milk protein composition, processing conditions (pasteurization and high-pressure treatment), and coagulants (camel chymosin, organic acids, plant proteases) on the quality of CM cheeses. CM cheese's weak texture is due to compositional characteristics of the milk, including low κ-casein-to-β-casein ratio (≈0.05 in CM vs. ≈0.33 in BM), large micelle size, different whey protein components, and higher proteolytic activity than BM. CM cheese texture can be improved by preheating the milk at low temperatures or by high pressure. Supplementing CM with calcium has shown inconsistent results on cheese texture, which may be due to interactions with other processing conditions. Despite their structure, CM cheeses are generally well liked in sensory studies.
Keywords: bovine milk cheese; camel milk cheese; coagulants; high pressure processing; pasteurization.
Copyright © 2022 Mbye, Ayyash, Abu-Jdayil and Kamal-Eldin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Faye B. How many large camelids in the world? A synthetic analysis of the world camel demographic changes. Pastoralism. (2020) 10:25. 10.1186/s13570-020-00176-z - DOI
-
- FAOSTAT . Food and Agriculture Data. FAOSTAT (2020). Available online at: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data (accessed December 1, 2021).
-
- Dairy Global . Dairy Global the Rise of Camel Milk. (2021). Retrieved from https://www.dairyglobal.net/industry-and-markets/market-trends/the-rise-... (accessed April 24, 2022).
-
- Solanki D, Hati S. Fermented camel milk: a review on its bio-functional properties. Emirates J Food Agric. (2018) 30:268–74. 10.9755/ejfa.2018.v30.i4.1661 - DOI
-
- Izadi A, Khedmat L, Mojtahedi SY. Nutritional and therapeutic perspectives of camel milk and its protein hydrolysates: a review on versatile bio functional properties. J Funct Foods. (2019) 60:103441. 10.1016/j.jff.2019.103441 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

