Chitosan/MCM-48 nanocomposite as a potential adsorbent for removing phenol from aqueous solution
- PMID: 35520349
- PMCID: PMC9054931
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra02960b
Chitosan/MCM-48 nanocomposite as a potential adsorbent for removing phenol from aqueous solution
Abstract
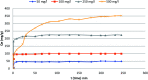
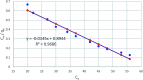
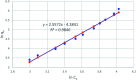
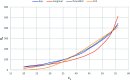
A new hybrid mesoporous nanocomposite (CMCM-48) based on chitosan and silica MCM-48 was considered as a potential adsorbent for removing phenol from aqueous solutions (toxic liquid waste) in a batch process. The new composite adsorbent was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms. The adsorption isotherm studies were analyzed using linear and nonlinear Langmuir, Freundlich and Dubinin-Radushkevich models for the optimum conditions when the initial phenol concentration, pH, adsorption temperature and time were 10-500 mg L-1, 3-10, 25.5 °C and 300 min, respectively. It was revealed that the experimental results agree well with the Dubinin-Radushkevich model, i.e. the correlation coefficient R 2 was 0.983085. The adsorption kinetics was modeled with linear and nonlinear pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order and intra particle diffusion kinetic models. The pseudo-second-order model was the best for describing the adsorption process with a correlation coefficient R 2 = 0.99925. The stability of the equilibrium data was studied for a phenol sorbent with a maximum adsorption capacity of 149.25 mg g-1. The results verified that the synthesized CMCM-48 was an efficient adsorbent for removing phenol from aqueous solutions.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures











References
-
- Sun X. Wang C. Li Y. Wang W. Wei J. Treatment of phenolic wastewater by combined UF and NF/RO processes. Desalination. 2015;355:68–74. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2014.10.018. - DOI
-
- Evans R., Revised Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (EPCRA), Section 313, Toxic Chemical Release reporting for calendar year 1998, Oak Ridge Y-12 Plant, TN (US), 2000
-
- Villegas L. G. C. Mashhadi N. Chen M. Mukherjee D. Taylor K. E. Biswas N. A short review of techniques for phenol removal from wastewater. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2016;2:157–167. doi: 10.1007/s40726-016-0035-3. - DOI
-
- Kazemi P. Peydayesh M. Bandegi A. Mohammadi T. Bakhtiari O. Stability and extraction study of phenolic wastewater treatment by supported liquid membrane using tributyl phosphate and sesame oil as liquid membrane. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2014;92:375–383. doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2013.07.023. - DOI
-
- Mohammadi S. Kargari A. Sanaeepur H. Abbassian K. Najafi A. Mofarrah E. Phenol removal from industrial wastewaters: a short review. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015;53:2215–2234. doi: 10.1080/19443994.2014.883327. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

