Fabrication of low-fouling, high-loading polymeric surfaces through pH-controlled RAFT
- PMID: 35520404
- PMCID: PMC9054213
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra02693j
Fabrication of low-fouling, high-loading polymeric surfaces through pH-controlled RAFT
Abstract
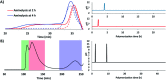
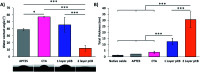
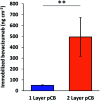
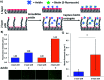
Low-fouling and high-loading surfaces are increasingly important for biosensing and blood purification technologies. Selective and efficient target binding from complex media can be achieved with poly(carboxybetaine) (pCB) surfaces that consist of a dense brush layer to resist non-specific protein adsorption and a sparse "mushroom" upper layer for high-density capture agent immobilization (i.e. high-loading). We developed pH-controlled surface-reversible addition-fragmentation chain-transfer (S-RAFT) polymerization to simplify fabrication of multi-modal, low-fouling and high-loading pCB surfaces without the need for quenching or re-initiation steps, toxic transition metals or light irradiation. Multi-modal polymer layers were produced through partial polymer termination by temporarily raising the pH to aminolyse a fraction of dormant chain transfer agents (CTAs); remaining polymer chains with intact CTAs continued uninterrupted extension to create the "mushroom" upper layer. The multi-modal pCB surfaces were low-fouling towards proteins (<6.7 ng cm-2), and macrophages. Compared to mono-modal brush surfaces, multi-modal pCB surfaces were high-loading with 5-fold greater capture agent immobilization (e.g. antibody) and 4-fold greater target binding (e.g. biotin-fluorescein).
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Erratum: Preparation of Poly(pentafluorophenyl acrylate) Functionalized SiO2 Beads for Protein Purification.J Vis Exp. 2019 Apr 30;(146). doi: 10.3791/6328. J Vis Exp. 2019. PMID: 31038480
-
Functionalizable and ultra-low fouling zwitterionic surfaces via adhesive mussel mimetic linkages.Biomaterials. 2010 Mar;31(7):1486-92. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.11.025. Epub 2009 Dec 4. Biomaterials. 2010. PMID: 19962753
-
Long-range interactions between protein-coated particles and POEGMA brush layers in a serum environment.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017 Feb 1;150:279-287. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.10.040. Epub 2016 Oct 24. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017. PMID: 28341156
-
PNIPAM grafted surfaces through ATRP and RAFT polymerization: Chemistry and bioadhesion.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017 Mar 1;151:143-155. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.12.007. Epub 2016 Dec 7. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017. PMID: 27992845 Review.
-
Aromatic Xanthates and Dithiocarbamates for the Polymerization of Ethylene through Reversible Addition-Fragmentation Chain Transfer (RAFT).Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019 Oct 1;58(40):14295-14302. doi: 10.1002/anie.201905629. Epub 2019 Aug 23. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019. PMID: 31328859 Review.
Cited by
-
Controlling Experimental Parameters to Improve Characterization of Biomaterial Fouling.Front Chem. 2020 Dec 11;8:604236. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2020.604236. eCollection 2020. Front Chem. 2020. PMID: 33363113 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

