The anti-diarrhea activity of red algae-originated sulphated polysaccharides on ETEC-K88 infected mice
- PMID: 35520502
- PMCID: PMC9059870
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra09247h
The anti-diarrhea activity of red algae-originated sulphated polysaccharides on ETEC-K88 infected mice
Abstract
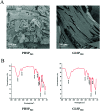
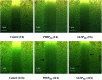
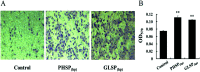
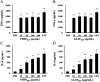
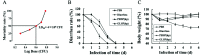
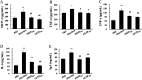
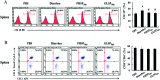
Polysaccharides from red algae Porphyra haitanensis and Gracilaria lemaneiformis possess various bioactive functions, however, their anti-diarrhea activity remains incompletely defined. In the current study, sulphated polysaccharides were extracted by high pressure treatment plus ethanol precipitation from these two algae, and named PHSP(hp) and GLSP(hp), respectively. PHSP(hp) and GLSP(hp) showed decreased viscosity and molecular weight. Meanwhile, they have a certain immunomodulatory effect on wound healing and migration of RAW264.7 cells. Moreover, they significantly increased the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). A BALB/c model infected by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC)-K88 was also established to evaluate the anti-diarrhea activity of PHSP(hp) and GLSP(hp). The results showed that PHSP(hp) and GLSP(hp) were able to alleviate mice diarrhea symptoms. Meanwhile, they inhibited the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and suppressed the secretion of immunoglobulin A via reducing the population of B cells. In addition, the nitroblue tetrazolium levels of mouse serum were decreased. Taken together, PHSP(hp) and GLSP(hp) alleviated the inflammatory response of ETEC-K88-induced diarrhea through both specific and non-specific immunity. Sulphated polysaccharides from red algae may be used as functional food components for remitting diarrhea.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fermented Gracilaria lemaneiformis polysaccharides alleviate food allergy by regulating Treg cells and gut microbiota.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Jun;269(Pt 2):132215. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.132215. Epub 2024 May 9. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38729482
-
Dietary fermented soybean meal replacement alleviates diarrhea in weaned piglets challenged with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88 by modulating inflammatory cytokine levels and cecal microbiota composition.BMC Vet Res. 2020 Jul 14;16(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s12917-020-02466-5. BMC Vet Res. 2020. PMID: 32664940 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Food Allergic Activity of Sulfated Polysaccharide from Gracilaria lemaneiformis is Dependent on Immunosuppression and Inhibition of p38 MAPK.J Agric Food Chem. 2016 Jun 8;64(22):4536-44. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b01086. Epub 2016 May 26. J Agric Food Chem. 2016. PMID: 27186807
-
Inhibitory Effect of Depolymerized Sulfated Galactans from Marine Red Algae on the Growth and Adhesion of Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli.Mar Drugs. 2019 Dec 10;17(12):694. doi: 10.3390/md17120694. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31835446 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal receptors for adhesive fimbriae of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) K88 in swine--a review.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2000 Sep;54(3):311-8. doi: 10.1007/s002530000404. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2000. PMID: 11030565 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent progress in Porphyra haitanensis polysaccharides: Extraction, purification, structural insights, and their impact on gastrointestinal health and oxidative stress management.Food Chem X. 2024 Apr 26;22:101414. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101414. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Food Chem X. 2024. PMID: 38711774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-cancer effects of Porphyra haitanensis polysaccharides on human colon cancer cells via cell cycle arrest and apoptosis without causing adverse effects in vitro.3 Biotech. 2020 Sep;10(9):386. doi: 10.1007/s13205-020-02379-y. Epub 2020 Aug 11. 3 Biotech. 2020. PMID: 32832336 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Mechanisms of Red Algae-Derived Bioactive Compounds in Alzheimer's Disease: An Overview of Novel Insights.Mar Drugs. 2025 Jun 30;23(7):274. doi: 10.3390/md23070274. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40710500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bifidobacterium longum, Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus acidilactici Reversed ETEC-Inducing Intestinal Inflammation in Mice.Microorganisms. 2022 Nov 28;10(12):2350. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10122350. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36557603 Free PMC article.
-
Preventive Effect of Depolymerized Sulfated Galactans from Eucheuma serra on Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-Caused Diarrhea via Modulating Intestinal Flora in Mice.Mar Drugs. 2021 Feb 1;19(2):80. doi: 10.3390/md19020080. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33535475 Free PMC article.
References
-
- GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators, Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015, Lancet, 2016, 388, 1545–1602. - PMC - PubMed
-
- English A. I. New frontiers in the development of vaccines against enterotoxinogenic (ETEC) and enterohaemorrhagic (EHEC) E. coli infections. Part II. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 1999;74:105–111. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

