Protective effects of Vinca herbaceous extract against scopolamine-induced behavioral disturbances and brain oxidative stress in rats
- PMID: 35520614
- PMCID: PMC9061637
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09295
Protective effects of Vinca herbaceous extract against scopolamine-induced behavioral disturbances and brain oxidative stress in rats
Abstract
Ethnopharmacological relevance: Alzheimer's disease (AD) as the most common type of dementia, is affecting the life of many senior individuals around the world. Vinca herbacea Waldst. & Kit. (V. herbacea) as a middle east originated plant demonstrated antioxidant and antitumor effects. This plant traditionally used to treat diabetes and hypertension, but its mechanism remains unclear.
Aim of the study: In the present study, post-treatment effects of V. herbacea on learning and memory functions, antioxidant cellular defense and oxidative stress were investigated using the scopolamine rat model of AD.
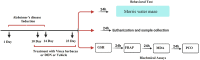
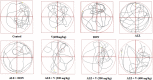
Materials and methods: Wistar male rats (170-190 g) were administered Scopolamine, an anti-muscarinic drug, (2 mg/kg) for 10 days followed by V. herbacea extract (200, 300 and 400 mg/kg) and/or donepezil (DON; 1 mg/kg, which were administered before behavioral studies for 10 consecutive days. All the rats were then subjected to Morris water maze (MWM) task. Biochemical parameters of oxidative stress were quantified using the whole brain.
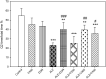
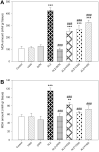
Results: Our data showed significant decrease performance in target quadrant in water maze task following administration of scopolamine (SCOP). Also, V. herbacea and DON, did not induce any neurotoxicity and hepatotoxic effects at the highest utilized doses in healthy rats. Treatment with V. herbacea extract (200&400 mg/kg) and DON improved memory performance significantly in comparison with AD rats. In addition, V. herbacea extract in AD rats exhibited a decrease in malondialdehyde (MDA) and protein carbonyl (PCO) levels and an increase in total antioxidant capacity (FRAP) and glutathione (GSH) amounts in brain and liver.
Conclusion: It seems that cholinergic deficits and oxidative stress are consistently associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD). The richness of V. herbacea in case of indole alkaloids and flavonoids confirms the potentials of this herb in management of oxidative stress, resorting synaptic acetylcholine level and improving cellular antioxidant resources.
Keywords: Hepatotoxicity; Indole alkaloids; Memory impairment; Neurotoxicity; Scopolamine; Vinca herbacea extract.
© 2022 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effects of empagliflozin against scopolamine-induced memory impairment and oxidative stress in rats.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2025 Jan 10;18:163-170. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2025.01.008. eCollection 2025 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39896712 Free PMC article.
-
Thymus daenensis extract prevents scopolamine‑induced memory impairment through declining oxidative stress in rats.Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2022;82(3):380-388. doi: 10.55782/ane-2022-036. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2022. PMID: 36214720
-
Ameliorative effect of kolaviron, a biflavonoid complex from Garcinia kola seeds against scopolamine-induced memory impairment in rats: role of antioxidant defense system.Metab Brain Dis. 2017 Feb;32(1):235-245. doi: 10.1007/s11011-016-9902-2. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Metab Brain Dis. 2017. PMID: 27631100
-
Effect of Cinnamomum zeylanicum extract on scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment and oxidative stress in rats.Nutr Neurosci. 2015 Jul;18(5):210-6. doi: 10.1179/1476830514Y.0000000113. Epub 2014 Feb 21. Nutr Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 24559058
-
Ameliorative effects of Matricaria chamomilla L. hydroalcoholic extract on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in rats: A behavioral and molecular study.Phytomedicine. 2018 Aug 1;47:113-120. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.04.049. Epub 2018 May 7. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30166095
Cited by
-
The role of gender differences in the outcome of juvenile social isolation: Emphasis on changes in behavioral, biochemical and expression of nitric oxide synthase genes alteration.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 1;10(7):e28964. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28964. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38617928 Free PMC article.
-
Promising neuroprotective potential of naringenin against trimethyltin-induced cognitive deficits and hippocampal neurodegeneration in rats.Front Neurosci. 2025 May 23;19:1567236. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1567236. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40486726 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effect of ranolazine improves behavioral discrepancies in a rat model of scopolamine-induced dementia.Front Neurosci. 2024 Jan 12;17:1267675. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1267675. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38323121 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effects of empagliflozin against scopolamine-induced memory impairment and oxidative stress in rats.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2025 Jan 10;18:163-170. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2025.01.008. eCollection 2025 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39896712 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing the Neuroprotection Potential of Edaravone in Transient Global Ischemia Treatment with Glutathione- (GSH-) Conjugated Poly(methacrylic acid) Nanogel as a Promising Carrier for Targeted Brain Drug Delivery.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023 Feb 21;2023:7643280. doi: 10.1155/2023/7643280. eCollection 2023. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023. PMID: 36865347 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmadi N., Hosseini M.-J., Rostamizadeh K., Anoush M. Investigation of therapeutic effect of curcumin α and β glucoside anomers against Alzheimer’s disease by the nose to brain drug delivery. Brain Res. 2021;1766:147517. - PubMed
-
- Akhani H. Flora Iranica: facts and figures and a list of publications by KH Rechinger on Iran and adjacent areas. Rostaniha. 2006;7(Suppl 2):19–61.
-
- Amiri S., Yousefi-Ahmadipour A., Hosseini M.-J., Haj-Mirzaian A., Momeny M., Hosseini-Chegeni H., Mokhtari T., Kharrazi S., Hassanzadeh G., Amini S.M. Maternal exposure to silver nanoparticles are associated with behavioral abnormalities in adulthood: role of mitochondria and innate immunity in developmental toxicity. Neurotoxicology. 2018;66:66–77. - PubMed
-
- Benzie I.F., Strain J.J. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: the FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996;239(1):70–76. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

