An expeditious click approach towards the synthesis of galactose coated novel glyco-dendrimers and dentromers utilizing a double stage convergent method
- PMID: 35520637
- PMCID: PMC9056565
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra05289b
An expeditious click approach towards the synthesis of galactose coated novel glyco-dendrimers and dentromers utilizing a double stage convergent method
Abstract
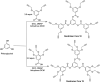
The primary motive behind this article is to bring to the forefront a unique kind of dendrimer which has remained a dark horse since its discovery, namely dentromer. We herein report the synthesis of glycodendrimers and glycodentromers crowned with galactose units by harnessing an expeditious synthesis of dendrimer core 18 and dentromer core 19, divergently with branching directionality (1 → 2) and (1 → 3), respectively. A competent, double stage convergent synthetic path was chosen to facilitate ease of refining and spectroscopic elucidations. By exploiting a Cu(i)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) reaction strategy, we successfully developed a new series of galactosylated dendrimers 20, 21, 22, and 24 containing 6, 12, 18, and 18 peripheral galactose units, respectively. We are first to report the practical synthesis of 9-peripheral galactose coated glycodentromer 23 (0th generation) and 27-peripheral galactose coated glycodentromer 25 (1st generation). These synthesized scaffolds were characterized by spectral studies such as 1H, 13C NMR, FT-IR, MALDI-TOF MS, HRMS and SEC analysis. Additionally, gel permeation chromatography depicted the regular progression in size from 6 to 27-peripheral galactose coated glycodendrimers along with glycodentromers, with their high monodispersity. Also, the glyco-dendrimers and dentromers synthesized from two different hypercore units i.e. dendrimers core (18) and dentromer core (19), have been supported by their UV-visible absorbance and emission spectroscopy.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures







Similar articles
-
CuAAC mediated synthesis of cyclen cored glycodendrimers of high sugar tethers at low generation.Carbohydr Res. 2021 Oct;508:108403. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2021.108403. Epub 2021 Jul 24. Carbohydr Res. 2021. PMID: 34329845
-
Electron Flow in Large Metallomacromolecules and Electronic Switching of Nanoparticle Stabilization: Click Ferrocenyl Dentromers that Reduce AuIII to Au Nanoparticles.Chemistry. 2018 Aug 27;24(48):12686-12694. doi: 10.1002/chem.201802289. Epub 2018 Jul 18. Chemistry. 2018. PMID: 29863753
-
Click chemistry inspired synthesis of glycoporphyrin dendrimers.J Org Chem. 2013 Aug 16;78(16):8184-90. doi: 10.1021/jo4012392. Epub 2013 Aug 5. J Org Chem. 2013. PMID: 23862720
-
Dentromers, a Family of Super Dendrimers with Specific Properties and Applications.Molecules. 2018 Apr 20;23(4):966. doi: 10.3390/molecules23040966. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29677169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Click dendrimers and triazole-related aspects: catalysts, mechanism, synthesis, and functions. A bridge between dendritic architectures and nanomaterials.Acc Chem Res. 2012 Apr 17;45(4):630-40. doi: 10.1021/ar200235m. Epub 2011 Dec 8. Acc Chem Res. 2012. PMID: 22148925 Review.
Cited by
-
Precision dendritic-supramolecular glycan assemblies for probing multivalent lectin interactions.Chem Sci. 2025 Jun 25;16(30):13636-13645. doi: 10.1039/d5sc03534a. eCollection 2025 Jul 30. Chem Sci. 2025. PMID: 40636579 Free PMC article.
-
Click Chemistry for Biofunctional Polymers: From Observing to Steering Cell Behavior.Chem Rev. 2024 Dec 11;124(23):13216-13300. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.4c00251. Epub 2024 Dec 2. Chem Rev. 2024. PMID: 39621547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Nanocarrier-based Approaches to Atopic Dermatitis and Emerging Trends in Drug Development and Design.Curr Drug Deliv. 2024;21(7):932-960. doi: 10.2174/1567201820666230508121716. Curr Drug Deliv. 2024. PMID: 37157192 Review.
-
Target-Specific Delivery and Bioavailability of Pharmaceuticals via Janus and Dendrimer Particles.Pharmaceutics. 2023 May 29;15(6):1614. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15061614. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37376062 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tomalia D. A. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2005;30:294–324. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2005.01.007. - DOI
- Grayson S. M. Fréchet J. M. J. Chem. Rev. 2001;101:3819–3867. doi: 10.1021/cr990116h. - DOI - PubMed
- Newkome G. R. Shreiner C. Chem. Rev. 2010;110:6338–6442. doi: 10.1021/cr900341m. - DOI - PubMed
- Majoral J.-P. Caminade A.-M. Chem. Rev. 1999;99:845–880. doi: 10.1021/cr970414j. - DOI - PubMed
- Wang D. Deraedt C. Ruiz J. Astruc D. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015;48:1871–1880. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.5b00039. - DOI - PubMed
- Sowinska M. Urbanczyk-Lipkowska Z. New J. Chem. 2014;38:2168–2203. doi: 10.1039/C3NJ01239E. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

