Novel mono-lipidated dimeric glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist with improved long-acting and hypoglycemic activity
- PMID: 35520704
- PMCID: PMC9062351
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra00833k
Novel mono-lipidated dimeric glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist with improved long-acting and hypoglycemic activity
Abstract
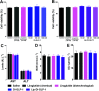
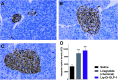
Dimerization is a useful tool to boost ligand-receptor interaction. Both lipidation and dimerization effectively prolong the short half-life (t 1/2) of peptides by facilitating binding with serum albumin and increasing hydrodynamic size. Here, we described two novel GLP-1 conjugates with high glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor activation potencies, dimerized GLP-1 (Di-GLP-1) and lipidated Di-GLP-1 (Lip-Di-GLP-1). Di-GLP-1 and Lip-Di-GLP-1 were prepared through cysteine-maleimide specific coupling reactions using Gly8-Cys31-GLP-1, bis-maleimide amine, and activated palmitic acid. The receptor activation potencies of Di-GLP-1 and Lip-Di-GLP-1 were 13.6-fold and 9.5-fold higher than GLP-1, respectively. The in vivo hypoglycemic and insulinotropic activities of Di-GLP-1 and Lip-Di-GLP-1 were also better than GLP-1 in db/db mice. Furthermore, Lip-Di-GLP-1 was found to have greater circulating t 1/2 than synthesized liraglutide by 1.8-fold. Accordingly, the improved pharmacokinetic profiles of Lip-Di-GLP-1 resulted in protracted antidiabetic effects as confirmed by hypoglycemic duration test. Moreover, Lip-Di-GLP-1 administered in mice potently inhibits gastric emptying and reduce food intake. Chronic Lip-Di-GLP-1 treatment in db/db mice resulted in significant improvements in food intake, body weight, pancreatic function and corrected hyperglycemia, which was more effective than synthesized liraglutide. Our research indicated that combined dimerization and lipidation were effectively applied to GLP-1, and the preclinical results suggested the potential usage of Lip-Di-GLP-1 as a long-acting antidiabetic agent.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Rational design of dimeric lipidated Xenopus glucagon-like peptide 1 analogues as long-acting antihyperglycaemic agents.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Sep 5;157:177-187. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.07.072. Epub 2018 Aug 3. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 30096651
-
Preparation and Pharmaceutical Characterizations of Lipidated Dimeric Xenopus Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Conjugates.Bioconjug Chem. 2018 Feb 21;29(2):390-402. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.7b00712. Epub 2018 Jan 9. Bioconjug Chem. 2018. PMID: 29239601
-
Novel mono-PEGylated dimeric GLP-1 conjugate with enhanced receptor activation and prolonged anti-diabetes efficacies.Life Sci. 2020 Aug 1;254:117752. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117752. Epub 2020 May 5. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32387412
-
Beyond glucose lowering: glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, body weight and the cardiovascular system.Diabetes Metab. 2011 Dec;37(6):477-88. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2011.07.001. Epub 2011 Aug 25. Diabetes Metab. 2011. PMID: 21871831 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of high-dose glucagon-like peptide-1, glucagon-like peptide-1/glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide, and glucagon-like peptide-1/glucagon receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2022 May;24(5):788-805. doi: 10.1111/dom.14640. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2022. PMID: 34984793 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

