Novel magnetically separable anhydride-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2@PEI-NTDA nanoparticles as effective adsorbents: synthesis, stability and recyclable adsorption performance for heavy metal ions
- PMID: 35520722
- PMCID: PMC9062167
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra10310k
Novel magnetically separable anhydride-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2@PEI-NTDA nanoparticles as effective adsorbents: synthesis, stability and recyclable adsorption performance for heavy metal ions
Abstract
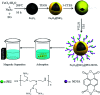
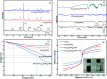
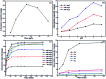
In this paper, a novel adsorbent, Fe3O4@SiO2@PEI-NTDA, was first prepared by the immobilization of an amine and anhydride onto magnetic Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles with polyethylenimine (PEI) and 1,4,5,8-naphthalenetetracarboxylic-dianhydride (NTDA) for the removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions. The structure of Fe3O4@SiO2@PEI-NTDA was systematically investigated; the results confirmed that amine and anhydride groups were successfully covalently grafted onto the surface of Fe3O4@SiO2, which showed a homogenous core-shell structure with three layers of about 300 nm diameter (Fe3O4 core: 200 nm, nSiO2 layer: 20 nm, and PEI-NTDA layer: 20 nm). The adsorption performance of Fe3O4@SiO2@PEI-NTDA NPs was evaluated for single Pb2+ and coexisting Cd2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, and Zn2+ ions in an aqueous solution in a batch system. The amine and anhydride groups may have a synergistic effect on Pb2+ removal through electrostatic interactions and chelation; Fe3O4@SiO2@PEI-NTDA NPs exhibited preferable removal of Pb2+ with maximum adsorption capacity of 285.3 mg g-1 for Pb2+ at a solution pH of 6.0, adsorbent dosage of 0.5 g L-1, initial Pb2+ concentration of 200 mg L-1 and contact time of 3 h. The adsorption mechanism conformed well to the Langmuir isotherm model, and the adsorption kinetic data were found to fit the pseudo-second order model. Fe3O4@SiO2@PEI-NTDA NPs could be recovered easily from their dispersion by an external magnetic field and demonstrated good recyclability and reusability for at least 6 cycles with a high adsorption capacity above 204.5 mg g-1. The magnetic adsorbents showed high stability with a weight loss below 0.65% in the acid leaching treatment by 2 M HCl solution for 144 h. This study indicates that Fe3O4@SiO2@PEI-NTDA NPs are new promising adsorbents for the effective removal of Pb2+ in wastewater treatment.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures





References
-
- Peer F. E. Bahramifar N. Younesi H. Removal of Cd (II), Pb (II) and Cu (II) ions from aqueous solution by polyamidoamine dendrimer grafted magnetic graphene oxide nanosheets. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018;87:225–240. doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2018.03.039. - DOI
-
- Medina R. P. Nadres E. T. Ballesteros F. C. Rodrigues D. F. Incorporation of graphene oxide into a chitosan-poly(acrylic acid) porous polymer nanocomposite for enhanced lead adsorption. Environ. Sci.: Nano. 2016;3:638–646. doi: 10.1039/C6EN00021E. - DOI
-
- Marani D. Macchi G. Pagano M. Lead precipitaiton in the presence of sulphate and carbonate, testing the thermodynamic predictions. Water Res. 1995;29(4):1085–1092. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(94)00232-V. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

