Xiao Qing Long Tang essential oil exhibits inhibitory effects on the release of pro-inflammatory mediators by suppressing NF-κB, AP-1, and IRF3 signalling in the lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells
- PMID: 35520778
- PMCID: PMC9063779
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra01448a
Xiao Qing Long Tang essential oil exhibits inhibitory effects on the release of pro-inflammatory mediators by suppressing NF-κB, AP-1, and IRF3 signalling in the lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells
Abstract
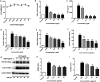
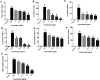
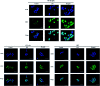
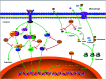
Xiao Qing Long Tang (literally "Minor blue dragon decoction" in Chinese), a traditional Chinese formula, is prescribed to treat respiratory diseases. However, only few studies have been reported on its anti-inflammatory mechanisms. In this study, we investigated the inhibitory effects of Xiao Qing Long Tang essential oil on inflammatory mediators and explored the mechanisms of action of XQEO in the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. XQEO was prepared via steam distillation and characterized by GC-MS analysis. MTT and Griess assays were used to measure cell viability and NO production, respectively. The mRNA expression and the production of LPS-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-10) and chemokines (MCP-1, Rantes, and MIP-1α) were determined by real-time PCR and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, respectively. Furthermore, we determined the protein levels of the components of NF-κB, AP-1 and IRF3 signalling by Western blotting. Immunofluorescence assay was used to estimate the nuclear translocation of NF-κB, AP-1 and IRF3. The results showed that XQEO inhibited the secretion of NO and PGE2 and down-regulated the mRNA and protein levels of iNOS and COX-2. We also found that XQEO suppressed the LPS-induced overproduction of pro-inflammatory mediators. Moreover, XQEO inhibited the phosphorylation of NF-κB/p65, AP-1/c-Jun, and IRF3 by suppressing their upstream kinases, such as MAPKs, TBK1, Akt, IKKα/β, and IκB, reducing the LPS-induced NF-κB, AP-1 and IRF3 translocation to the nucleus. These findings suggest that XQEO effectively suppresses the production of pro-inflammatory mediators possibly through the inhibition of NF-κB, AP-1, and IRF3 signalling in the LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dingchuan tang essential oil inhibits the production of inflammatory mediators via suppressing the IRAK/NF-κB, IRAK/AP-1, and TBK1/IRF3 pathways in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Sep 4;12:2731-2748. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S160645. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 30233137 Free PMC article.
-
Schisandra Chinensis Lignans Suppresses the Production of Inflammatory Mediators Regulated by NF-κB, AP-1, and IRF3 in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells.Molecules. 2018 Dec 14;23(12):3319. doi: 10.3390/molecules23123319. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30558163 Free PMC article.
-
An ethanolic extract of the aerial part of Siegesbeckia orientalis L. inhibits the production of inflammatory mediators regulated by AP-1, NF-κB and IRF3 in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells.Biosci Trends. 2018;12(3):330-337. doi: 10.5582/bst.2018.01103. Biosci Trends. 2018. PMID: 30012916
-
Re-Du-Ning inhalation solution exerts suppressive effect on the secretion of inflammatory mediators via inhibiting IKKα/β/IκBα/NF-κB, MAPKs/AP-1, and TBK1/IRF3 signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages.RSC Adv. 2019 Mar 18;9(16):8912-8925. doi: 10.1039/c9ra00060g. eCollection 2019 Mar 15. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35517648 Free PMC article.
-
A herbal formula comprising Rosae Multiflorae Fructus and Lonicerae Japonicae Flos inhibits the production of inflammatory mediators and the IRAK-1/TAK1 and TBK1/IRF3 pathways in RAW 264.7 and THP-1 cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Nov 4;174:195-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.08.018. Epub 2015 Aug 20. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26297845
Cited by
-
Adding Chinese Herbal Medicine to Routine Care is Associated With a Lower Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis Among Patients With Asthma: A Population-Based Retrospective Cohort Study.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 17;13:895717. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.895717. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36059972 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying the Chinese Herbal Medicine Network and Core Formula for Allergic Rhinitis on a Real-World Database.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Nov 5;2020:5979708. doi: 10.1155/2020/5979708. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 33204289 Free PMC article.
-
Acetylation of TIR domains in the TLR4-Mal-MyD88 complex regulates immune responses in sepsis.EMBO J. 2024 Nov;43(21):4954-4983. doi: 10.1038/s44318-024-00237-8. Epub 2024 Sep 18. EMBO J. 2024. PMID: 39294473 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Essential Oils on the Release of TNF-α and CCL2 by LPS-Stimulated THP‑1 Cells.Plants (Basel). 2020 Dec 28;10(1):50. doi: 10.3390/plants10010050. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33379375 Free PMC article.
-
Edgeworthia gardneri (Wall.) Meisn. Water Extract Ameliorates Palmitate Induced Insulin Resistance by Regulating IRS1/GSK3β/FoxO1 Signaling Pathway in Human HepG2 Hepatocytes.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jan 30;10:1666. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01666. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32082162 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

