Reactive intermediates in naquotinib metabolism identified by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: phase I metabolic profiling
- PMID: 35520926
- PMCID: PMC9062305
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra00224c
Reactive intermediates in naquotinib metabolism identified by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: phase I metabolic profiling
Abstract
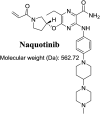
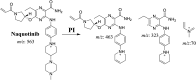
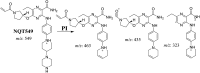
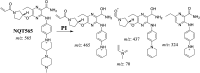
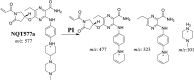
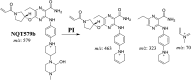
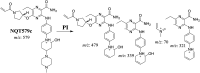
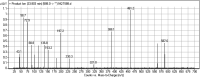
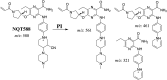
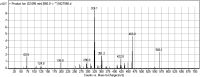
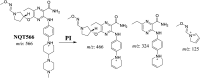
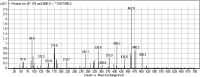
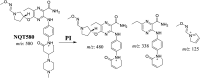
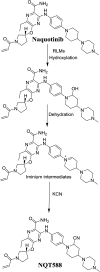
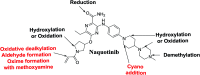
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are very efficient for the treatment of EGFR-mutated lung cancer and show improved therapeutic efficacy. However, treatment with both first- and second-generation TKIs results in acquired resistance and is related to various toxicities; the EGFR T790M mutation has been associated with this resistance. Naquotinib (ASP8273, NQT) is a novel third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor that has been shown to be more potent than osimertinib in the management of L858R plus T790M mutations. However, its bioactivation may occur and promote the formation of reactive electrophiles that are toxic. We hypothesize that these reactive intermediates are potentially involved in the side effects of NQT. Reactive metabolites are often formed by phase I metabolic reactions and cannot be characterized directly as they are transient in nature. Using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), we screened for in vitro metabolites of NQT formed during incubation with human liver microsomes and evaluated the generation of reactive electrophiles using capturing agents, such as methoxyamine and potassium cyanide, as nucleophiles that form stable adducts for identification by LC-MS/MS. Eight NQT phase I metabolites were found that had been formed by N-demethylation, oxidation, hydroxylation, and reduction. In addition, three reactive electrophiles, two aldehydes, and one iminium ion were identified, and the corresponding bioactivation mechanisms were proposed. The reported side effects of NQT may be related to the generation of reactive metabolites. Based on a literature review, this may be the first study of in vitro phase I metabolites, detailed structural characterizations, and NQT reactive intermediates.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A simple liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method to accurately determine the novel third-generation EGFR-TKI naquotinib with its applicability to metabolic stability assessment.RSC Adv. 2019 Feb 7;9(9):4862-4869. doi: 10.1039/c8ra09812c. eCollection 2019 Feb 5. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35514667 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry metabolic profiling of nazartinib reveals the formation of unexpected reactive metabolites.R Soc Open Sci. 2019 Aug 14;6(8):190852. doi: 10.1098/rsos.190852. eCollection 2019 Aug. R Soc Open Sci. 2019. PMID: 31598253 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of Fenebrutinib Metabolism and Bioactivation Using MS3 Methodology in Ion Trap LC/MS.Molecules. 2023 May 22;28(10):4225. doi: 10.3390/molecules28104225. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37241965 Free PMC article.
-
Osimertinib: A third-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor for treatment of epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated non-small cell lung cancer with the acquired Thr790Met mutation.J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2018 Jul;24(5):379-388. doi: 10.1177/1078155217712401. Epub 2017 May 31. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2018. PMID: 28565936 Review.
-
Can we define the optimal sequence of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant nonsmall cell lung cancer?Curr Opin Oncol. 2017 Mar;29(2):89-96. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0000000000000350. Curr Opin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28085680 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Iminium Intermediates Generation in the Metabolism of Tepotinib Using LC-MS/MS: In Silico and Practical Approaches to Bioactivation Pathway Elucidation.Molecules. 2020 Oct 28;25(21):5004. doi: 10.3390/molecules25215004. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33126762 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ettinger D. S. Akerley W. Bepler G. Blum M. G. Chang A. Cheney R. T. Chirieac L. R. D'Amico T. A. Demmy T. L. Ganti A. K. P. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Network. 2010;8:740–801. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

