Preparation and biocompatibility of Fe50Ni50p/HAP/PEEK biocomposites with weak magnetic properties
- PMID: 35520933
- PMCID: PMC9062304
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra00719a
Preparation and biocompatibility of Fe50Ni50p/HAP/PEEK biocomposites with weak magnetic properties
Abstract
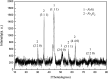
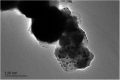
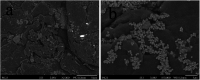
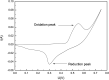
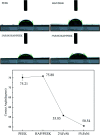
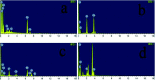
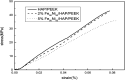
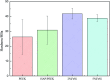
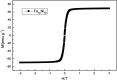
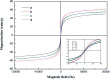
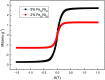
Hydroxyapatite (HAP)/polyetheretherketone (PEEK) composites are widely used in the new generation of bone implant materials. The use of weak magnetic fields can promote the biocompatibility of PEEK materials. In this paper, Fe50Ni50 alloy nanopowders and Fe50Ni50/HAP/PEEK composites were prepared by liquid phase chemical reduction and liquid phase mixing. The prepared Fe50Ni50 alloy nanopowders have a particle size of about 100 nm and good chemical activity and magnetic properties. The saturation magnetization (M s) of the Fe50Ni50 alloy powders is 70 emu g-1. Fe50Ni50 nano-powders in Fe50Ni50/HAP/PEEK composites are uniformly distributed in the matrix in the form of individual particles, achieving nano-level dispersion. With the increase of Fe50Ni50 alloy powders content, the magnetic properties of the composites are significantly enhanced. The biocompatibility of Fe50Ni50/HAP/PEEK composites is significantly better than that of PEEK and HAP/PEEK materials. The 2% Fe50Ni50/HAP/PEEK composite has the best comprehensive performance, and its biocompatibility is good. The contact angle is only 55.85°. The M s reaches 1.5 emu g-1 and the hardness reaches 42 HBa.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

