Design, synthesis and in silico studies of new quinazolinone derivatives as antitumor PARP-1 inhibitors
- PMID: 35521104
- PMCID: PMC9055986
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra05943a
Design, synthesis and in silico studies of new quinazolinone derivatives as antitumor PARP-1 inhibitors
Abstract
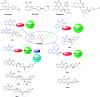
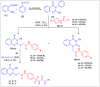
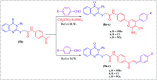
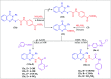
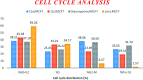
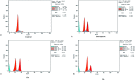
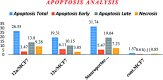
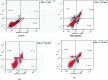
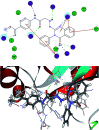
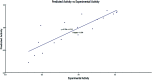
Herein, we report an eco-friendly synthesis of a new series of quinazolinone-based derivatives as potential PARP-1 inhibitors. The 4-quinazolinone scaffold was utilized as a bioisostere to the phthalazinone core of the reference compound Olaparib. Most of the synthesized compounds displayed appreciable inhibitory activity against PARP-1. Compound 12c showed inhibitory activity at IC50 = 30.38 nM comparable to Olaparib, which has IC50 = 27.89 nM. Cell cycle analysis was performed for compounds 12a and 12c, and both exhibited cell growth arrest at G2/M phase in the MCF-7 cell line. In addition, both compounds increased the programmed apoptosis compared to the control. Furthermore, molecular docking of the final compounds into the PARP-1 active site was executed to explore their probable binding modes. Also, a computational QSAR and in silico ADMET study was performed. The results of this study revealed that some of the newly synthesized compounds could serve as a new framework to discover new PARP-1 inhibitors with anti-cancer activity.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures
References
-
- Comen E. A. and Robson M.. Oncology, Williston Park, N.Y., 2010, vol. 24, pp. 55–62 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

