A 3D mixing-based portable magnetic device for fully automatic immunofluorescence staining of γ-H2AX in UVC-irradiated CD4+ cells
- PMID: 35521108
- PMCID: PMC9055984
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra03925j
A 3D mixing-based portable magnetic device for fully automatic immunofluorescence staining of γ-H2AX in UVC-irradiated CD4+ cells
Abstract
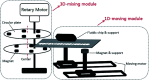
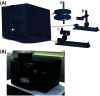
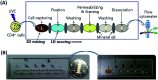
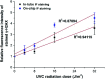
Immunofluorescence (IF) is a common method used in cell biology. The conventional protocol for IF staining is time and labor-intensive, operator dependent and reagent-consuming. Magnetic Bead (MB)-based microdevices are frequently utilized in cellular assays, but integration of simple and efficient mixing with downstream multi-step manipulation of MBs for automatic IF staining is still challenging. We herein present a portable, inexpensive and integratable device for MB-based automatic IF staining. First, a front-end cell capture step is performed using a 3D-mixing module, which is built upon a novel mechanism named ec-2MagRotors and generates periodically changing 3D magnetic fields. A 5-fold enhancement of cell capture efficiency was attained even with a low bead-to-cell concentration ratio (5 : 1), when conducting magnetic 3D mixing. Second, a 1D-moving module is employed downstream to automatically manipulate MB-cell complexes for IF staining. Further, a simplified protocol for staining of γ-H2AX, a biomarker widely used in evaluation of cell radiation damage, is presented for proof-of-principle study of the magnetic device. Using UVC-irradiated CD4+ cells as samples, our device achieved fully automatic γ-H2AX staining within 40 minutes at room temperature and showed a linear dose-response relationship. The developed portable magnetic device is automatic, efficient, cost-effective and simple-to-use, holding great potential for applications in different IF assays.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

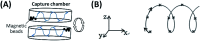


Similar articles
-
Biological in-vivo measurement of dose distribution in patients' lymphocytes by gamma-H2AX immunofluorescence staining: 3D conformal- vs. step-and-shoot IMRT of the prostate gland.Radiat Oncol. 2011 Jun 7;6:62. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-6-62. Radiat Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21649920 Free PMC article.
-
Fully Integrated Microfluidic Device for Magnetic Bead Manipulation to Assist Rapid Reaction and Cleaning.Anal Chem. 2023 Oct 10;95(40):14934-14943. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c02285. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Anal Chem. 2023. PMID: 37752733
-
Half brain irradiation in a murine model of breast cancer brain metastasis: magnetic resonance imaging and histological assessments of dose-response.Radiat Oncol. 2018 Jun 1;13(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s13014-018-1028-8. Radiat Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29859114 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma-H2AX-based dose estimation for whole and partial body radiation exposure.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e25113. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025113. Epub 2011 Sep 23. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21966430 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma-H2AX - a novel biomarker for DNA double-strand breaks.In Vivo. 2008 May-Jun;22(3):305-9. In Vivo. 2008. PMID: 18610740 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

