Novel biocompatible core/shell Fe3O4@NFC@Co(ii) as a new catalyst in a multicomponent reaction: an efficient and sustainable methodology and novel reusable material for one-pot synthesis of 4 H-pyran and pyranopyrazole in aqueous media
- PMID: 35521285
- PMCID: PMC9057109
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra04698a
Novel biocompatible core/shell Fe3O4@NFC@Co(ii) as a new catalyst in a multicomponent reaction: an efficient and sustainable methodology and novel reusable material for one-pot synthesis of 4 H-pyran and pyranopyrazole in aqueous media
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Novel biocompatible core/shell Fe3O4@NFC@Co(ii) as a new catalyst in a multicomponent reaction: an efficient and sustainable methodology and novel reusable material for one-pot synthesis of 4H-pyran and pyranopyrazole in aqueous media.RSC Adv. 2024 Jan 5;14(3):1673. doi: 10.1039/d3ra90127k. eCollection 2024 Jan 3. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38187448 Free PMC article.
Abstract
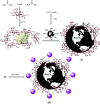
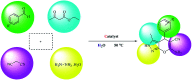
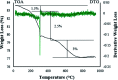
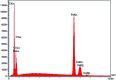
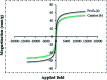
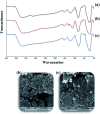
Today, due to the developing need for inexpensive catalysts, recyclable magnetic nanocatalysts immobilized on polysaccharides possess many advantages over classical heterogeneous catalysts. However, cellulose has been an appealing material in catalysis science and technology. In this work, by controlling the interaction between the inorganic complexes and the support material, we designed a high activity nanostructured combination of a magnetic nanoparticle Fe3O4@NFC@Co(ii) terminated complex as a multi-nuclear catalyst. This protocol involves an environment friendly approach using cobalt acetate. The magnetic nanostructure Fe3O4@NFC@Co(ii) can be used as a novel, green, and a powerful catalyst that demonstrates a short reaction time, high yield and easy procedure for the cascade Knoevenagel-Michael-cyclocondensation reaction for the one-pot synthesis of 4H-pyrans and pyranopyrazoles. The superparamagnetic nanocomposite could be conveniently separated by using an external magnet. Moreover, the catalyst could be reused at least five times in new reaction runs without a noticeable loss of activity. The prepared catalyst was characterized by FT-IR, XRD, VSM, FESEM, EDAX, TEM, ICP, and TGA techniques. The experiments were achieved with good yields and implied that the catalytic method was effective and convenient for heterocyclic synthesis.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures








References
-
- Moosavi-Zare A. R. Zolfigol M. A. Khaledian O. Khakyzadeh V. Farahani M. D. Kruger H. G. New J. Chem. 2014;38(6):2342–2347. doi: 10.1039/C3NJ01509B. - DOI
-
- Moosavi-Zare A. R. Zolfigol M. A. Khaledian O. Khakyzadeh V. Beyzavi M. H. Kruger H. G. Chem. Eng. J. 2014;248:122–127. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.03.035. - DOI
-
- Bakherad M. Keivanloo A. Amin A. H. Ghamari kargar P. Iran. J. Catal. 2018;3:179–187.
- Khazaei A. Moosavi-Zare A. R. Mohammadi Z. Khakyzadeh V. Afsar J. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2016;63(2):165–170. doi: 10.1002/jccs.201500384. - DOI
-
- Dabiri M. Salehi P. Otokesh S. Baghbanzadeh M. Kozehgary G. Mohammadi A. A. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005;46(36):6123–6126. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2005.06.157. - DOI
-
- Wender P. A. Handy S. T. Wright D. L. Chem. Ind. 1997:765.
- Trost B. M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 1995;34:259. doi: 10.1002/anie.199502591. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

