Rab33b-exocyst interaction mediates localized secretion for focal adhesion turnover and cell migration
- PMID: 35521520
- PMCID: PMC9061791
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104250
Rab33b-exocyst interaction mediates localized secretion for focal adhesion turnover and cell migration
Abstract
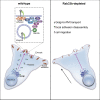
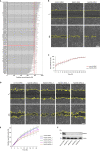
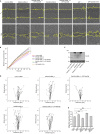
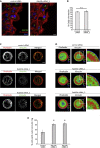
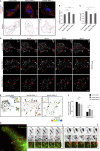
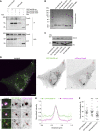
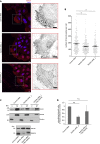
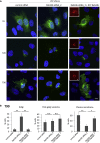
Rab proteins are well known regulators of intracellular trafficking; however, more and more studies point to their function also in other cellular processes, including cell migration. In this work, we have performed an siRNA screen to identify Rab proteins that influence cell migration. The screen revealed Rab33b as the strongest candidate that affected cell motility. Rab33b has been previously reported to localize at the Golgi apparatus to regulate Golgi-to-ER retrograde trafficking and Golgi homeostasis. We revealed that Rab33b also mediates post-Golgi transport to the plasma membrane. We further identified Exoc6, a subunit of the exocyst complex, as an interactor of Rab33b. Moreover, our data indicate that Rab33b regulates focal adhesion dynamics by modulating the delivery of cargo such as integrins to focal adhesions. Altogether, our results demonstrate a role for Rab33b in cell migration by regulating the delivery of integrins to focal adhesions through the interaction with Exoc6.
Keywords: Cell biology; Functional aspects of cell biology; Organizational aspects of cell biology.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
N.A.G. is now under paid employment by the company Thermo Fisher Scientific. Other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bartha A., Gyorffy B. TNMplot.com: a web tool for the comparison of gene expression in normal, tumor and metastatic tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:2622. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

