Scalable in-memory processing of omics workflows
- PMID: 35521547
- PMCID: PMC9052061
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.04.014
Scalable in-memory processing of omics workflows
Abstract
We present a proof of concept implementation of the in-memory computing paradigm that we use to facilitate the analysis of metagenomic sequencing reads. In doing so we compare the performance of POSIX™file systems and key-value storage for omics data, and we show the potential for integrating high-performance computing (HPC) and cloud native technologies. We show that in-memory key-value storage offers possibilities for improved handling of omics data through more flexible and faster data processing. We envision fully containerized workflows and their deployment in portable micro-pipelines with multiple instances working concurrently with the same distributed in-memory storage. To highlight the potential usage of this technology for event driven and real-time data processing, we use a biological case study focused on the growing threat of antimicrobial resistance (AMR). We develop a workflow encompassing bioinformatics and explainable machine learning (ML) to predict life expectancy of a population based on the microbiome of its sewage while providing a description of AMR contribution to the prediction. We propose that in future, performing such analyses in 'real-time' would allow us to assess the potential risk to the population based on changes in the AMR profile of the community.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Cloud; HPC; Key-value store; Machine learning; Metagenomics.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
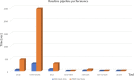
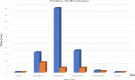
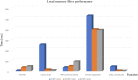
Figures







References
-
- Kintsakis A.M., Psomopoulos F.E., Symeonidis A.L., Mitkas P.A. Hermes: Seamless delivery of containerized bioinformatics workflows in hybrid cloud (htc) environments. SoftwareX. 2017;6:217–224. doi: 10.1016/j.softx.2017.07.007. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352711017300304. - DOI
-
- Gupta S., Imani M., Khaleghi B., Kumar V., Rosing T. 2019 IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Low Power Electronics and Design (ISLPED) 2019. Rapid: A reram processing in-memory architecture for dna sequence alignment; pp. 1–6. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
