A Pilot Study of Durvalumab (MEDI4736) with Tremelimumab in Combination with Image-Guided Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in the Treatment of Metastatic Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer
- PMID: 35521657
- PMCID: PMC9293682
- DOI: 10.1089/thy.2022.0050
A Pilot Study of Durvalumab (MEDI4736) with Tremelimumab in Combination with Image-Guided Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in the Treatment of Metastatic Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer
Abstract
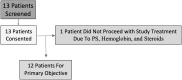
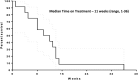
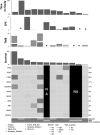
Background: Metastatic anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC) has a poor prognosis. This pilot study aims to evaluate tremelimumab plus durvalumab with stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) to improve overall survival (OS). Methods: Eligible patients received up to 4 doses tremelimumab (75 mg) given q4 weeks and up to 1 year of durvalumab (1500 mg) given q4 weeks. SBRT at 9 Gy × 3 fractions was given within the first 2 weeks of the start of treatment. Paired biopsies (pretreatment and between 3 and 10 weeks after the first dose of the drug treatment) were done in the medically qualified patients. Major inclusion criteria are metastatic ATC, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status 0-2, no prior immunotherapy, and last anticancer treatment >7 days before starting the study. The primary endpoint was 1 year OS with the combination of durvalumab, tremelimumab, and SBRT in metastatic ATC patients with a target of 1 year OS in ≥2 out of 12 patients. Results: A total of 13 patients signed consent but only 12 patients ultimately participated in this trial. One patient who consented to the protocol became ineligible for this study due to continued decline in performance status. Patient characteristics were as follows: male (n = 6) with a median age of 71 years (range: 49-82), and ECOG = 1. Nine patients had prior neck radiation and nine patients had prior chemotherapy. Next-generation sequencing and PD-L1 staining were done in the nine patients where tissue was available. High microsatellite instability (MSI) corresponding to mismatch repair defect was noted in two patients. There were zero confirmed responses and only one patient had stable disease and was treated with ≥4 cycles of study drugs. The median time that the patients were under treatment was 11 weeks (1-28 weeks). MSI status did not affect treatment response. High MSI patients were on treatment for 8-14 weeks before disease progression. The median OS was 14.5 weeks with only 1 patient alive beyond 1 year. The presence of a BRAF or p53 mutation did not appear to affect treatment outcome. Conclusions: Tremelimumab and durvalumab with SBRT did not improve OS for ATC. Future research is needed to examine other novel immunotherapy combinations with or without radiotherapy in the treatment of ATC. Clinical Trial Registration: NCT03122496.
Keywords: SBRT; anaplastic thyroid cancer; immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
N.Y.L. is on the advisory board—Merck, Merck EMD, Mirati, Elsie. N.R.: Research support: Repare, Repertoire, Invitae, Pfizer; Consulting paige. C.J.T. is on the Varian Advisory Board. All other authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Prasongsook N, Kumar A, Chintakuntlawar AV, et al. 2017. Survival in response to multimodal therapy in anaplastic thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 102:4506–4514. - PubMed
-
- Sherman EJ, Lim SH, Ho AL, et al. 2011. Concurrent doxorubicin and radiotherapy for anaplastic thyroid cancer: a critical re-evaluation including uniform pathologic review. Radiother Oncol 101:425–430. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

