Silyl formates as hydrosilane surrogates for the transfer hydrosilylation of ketones
- PMID: 35522145
- PMCID: PMC9476892
- DOI: 10.1039/d2cc00666a
Silyl formates as hydrosilane surrogates for the transfer hydrosilylation of ketones
Abstract
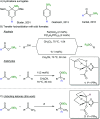
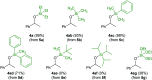
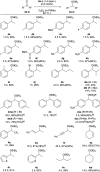
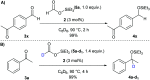
A transfer hydrosilylation of ketones employing silyl formates as hydrosilane surrogates under mild conditions is presented. A total of 24 examples of ketones have been successfully converted to their corresponding silyl ethers with 61-99% yields in the presence of a PNHP-based ruthenium catalyst and silyl formate reagent. The crucial role of the ligand for the transformation is demonstrated.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Amrein S. Studer A. Helv. Chim. Acta. 2002;85:3559. doi: 10.1002/1522-2675(200210)85:10<3559::AID-HLCA3559>3.0.CO;2-6. - DOI
- Amrein S. Timmermann A. Studer A. Org. Lett. 2001;3:2357. doi: 10.1021/ol016160c. - DOI - PubMed
- Studer A. Amrein S. 39 . Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2000:3080. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20000901)39:17<3080::AID-ANIE3080>3.0.CO;2-E. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

