Deletion of Schizophrenia Susceptibility Gene Ulk4 Leads to Abnormal Cognitive Behaviors via Akt-GSK-3 Signaling Pathway in Mice
- PMID: 35522199
- PMCID: PMC9212110
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbac040
Deletion of Schizophrenia Susceptibility Gene Ulk4 Leads to Abnormal Cognitive Behaviors via Akt-GSK-3 Signaling Pathway in Mice
Abstract
Objectives: Despite of strenuous research in the past decades, the etiology of schizophrenia (SCZ) still remains incredibly controversial. Previous genetic analysis has uncovered a close association of Unc-51 like kinase 4 (ULK4), a family member of Unc-51-like serine/threonine kinase, with SCZ. However, animal behavior data which may connect Ulk4 deficiency with psychiatric disorders, particularly SCZ are still missing.
Methods: We generated Emx1-Cre:Ulk4flox/flox conditional knockout (CKO) mice, in which Ulk4 was deleted in the excitatory neurons of cerebral cortex and hippocampus.
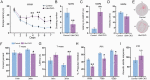
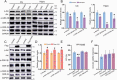
Results: The cerebral cellular architecture was maintained but the spine density of pyramidal neurons was reduced in Ulk4 CKO mice. CKO mice showed deficits in the spatial and working memories and sensorimotor gating. Levels of p-Akt and p-GSK-3α/β were markedly reduced in the CKO mice indicating an elevation of GSK-3 signaling. Mechanistically, Ulk4 may regulate the GSK-3 signaling via putative protein complex comprising of two phosphatases, protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) and 1α (PP1α). Indeed, the reduction of p-Akt and p-GSK-3α/β was rescued by administration of inhibitor acting on PP2A and PP1α in CKO mice.
Conclusions: Our data identified potential downstream signaling pathway of Ulk4, which plays important roles in the cognitive functions and when defective, may promote SCZ-like pathogenesis and behavioral phenotypes in mice.
Keywords: Akt; GSK-3; Unc-51-like kinase 4; cerebral cortex; schizophrenia; sensorimotor gating.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Maryland Psychiatric Research Center. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ulk4, a Newly Discovered Susceptibility Gene for Schizophrenia, Regulates Corticogenesis in Mice.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 21;9:645368. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.645368. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34235142 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor-2 deficiency induces schizophrenia-like behaviors in mice.Sci Rep. 2015 Feb 17;5:8502. doi: 10.1038/srep08502. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25687169 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent deletions of ULK4 in schizophrenia: a gene crucial for neuritogenesis and neuronal motility.J Cell Sci. 2014 Feb 1;127(Pt 3):630-40. doi: 10.1242/jcs.137604. Epub 2013 Nov 27. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 24284070
-
Schizophrenia predisposition gene Unc-51-like kinase 4 for the improvement of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Apr;49(4):2933-2943. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-07108-z. Epub 2022 Jan 27. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35083612
-
Applications and Possible Mechanisms of ULK4 in Brain: Implications for Neuropsychiatric Disorders.J Integr Neurosci. 2025 May 21;24(5):31350. doi: 10.31083/JIN31350. J Integr Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40464465 Review.
Cited by
-
DCC in the cerebral cortex is required for cognitive functions in mouse.Brain Pathol. 2025 May;35(3):e13306. doi: 10.1111/bpa.13306. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Brain Pathol. 2025. PMID: 39293934 Free PMC article.
-
A rat Satb1 truncation causes neurodevelopmental abnormalities recapitulating the symptoms of patients with SATB1 mutations.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 Jun 26. doi: 10.1038/s41401-025-01588-6. Online ahead of print. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 40571781
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

