Regulation of CLB6 expression by the cytoplasmic deadenylase Ccr4 through its coding and 3' UTR regions
- PMID: 35522675
- PMCID: PMC9075657
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268283
Regulation of CLB6 expression by the cytoplasmic deadenylase Ccr4 through its coding and 3' UTR regions
Abstract
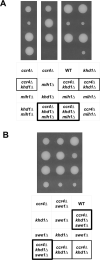
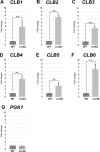
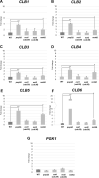
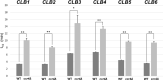
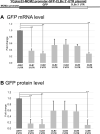
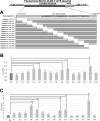
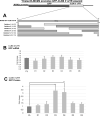
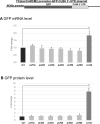
RNA stability control contributes to the proper expression of gene products. Messenger RNAs (mRNAs) in eukaryotic cells possess a 5' cap structure and the 3' poly(A) tail which are important for mRNA stability and efficient translation. The Ccr4-Not complex is a major cytoplasmic deadenylase and functions in mRNA degradation. The CLB1-6 genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae encode B-type cyclins which are involved in the cell cycle progression together with the cyclin-dependent kinase Cdc28. The CLB genes consist of CLB1/2, CLB3/4, and CLB5/6 whose gene products accumulate at the G2-M, S-G2, and late G1 phase, respectively. These Clb protein levels are thought to be mainly regulated by the transcriptional control and the protein stability control. Here we investigated regulation of CLB1-6 expression by Ccr4. Our results show that all CLB1-6 mRNA levels were significantly increased in the ccr4Δ mutant compared to those in wild-type cells. Clb1, Clb4, and Clb6 protein levels were slightly increased in the ccr4Δ mutant, but the Clb2, Clb3, and Clb5 protein levels were similar to those in wild-type cells. Since both CLB6 mRNA and Clb6 protein levels were most significantly increased in the ccr4Δ mutant, we further analyzed the cis-elements for the Ccr4-mediated regulation within CLB6 mRNA. We found that there were destabilizing sequences in both coding sequence and 3' untranslated region (3' UTR). The destabilizing sequences in the coding region were found to be both within and outside the sequences corresponding the cyclin domain. The CLB6 3' UTR was sufficient for mRNA destabilization and decrease of the reporter GFP gene and this destabilization involved Ccr4. Our results suggest that CLB6 expression is regulated by Ccr4 through the coding sequence and 3' UTR of CLB6 mRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
CLB5 and CLB6, a new pair of B cyclins involved in DNA replication in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1160-75. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1160. Genes Dev. 1993. PMID: 8319908
-
Among B-type cyclins only CLB5 and CLB6 promote premeiotic S phase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2012 Mar;190(3):1001-16. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.134684. Epub 2011 Dec 29. Genetics. 2012. PMID: 22209902 Free PMC article.
-
Negative regulation of G1 and G2 by S-phase cyclins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Sep;15(9):5030-42. doi: 10.1128/MCB.15.9.5030. Mol Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 7651421 Free PMC article.
-
Control of the yeast cell cycle by the Cdc28 protein kinase.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):166-79. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90099-c. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993. PMID: 8507488 Review.
-
Cytoplasmic deadenylation: regulation of mRNA fate.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Dec;38(6):1531-6. doi: 10.1042/BST0381531. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 21118121 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The RNA-binding protein Puf5 and the HMGB protein Ixr1 contribute to cell cycle progression through the regulation of cell cycle-specific expression of CLB1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.PLoS Genet. 2022 Jul 29;18(7):e1010340. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010340. eCollection 2022 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 35905103 Free PMC article.
-
Association between arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase gene polymorphisms and arsenic methylation capacity in rural residents of northern China: a cross-sectional study.Arch Toxicol. 2023 Nov;97(11):2919-2928. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03590-5. Epub 2023 Sep 2. Arch Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37658865
References
-
- Lodish H, Berk A, Kaiser CA, Krieger M, Bretscher A, Ploegh H, et al.. Molecular Cell Biology Eight Edition. W.H. Freeman and Company; 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

