The N6-methyladenosine modification enhances ferroptosis resistance through inhibiting SLC7A11 mRNA deadenylation in hepatoblastoma
- PMID: 35522946
- PMCID: PMC9076012
- DOI: 10.1002/ctm2.778
The N6-methyladenosine modification enhances ferroptosis resistance through inhibiting SLC7A11 mRNA deadenylation in hepatoblastoma
Abstract
Background: Solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11) is overexpressed in multiple human tumours and functions as a transporter importing cystine for glutathione biosynthesis. It promotes tumour development in part by suppressing ferroptosis, a newly identified form of cell death that plays a pivotal role in the suppression of tumorigenesis. However, the role and underlying mechanisms of SLC7A11-mediated ferroptosis in hepatoblastoma (HB) remain largely unknown.
Methods: Reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) and western blotting were used to measure SLC7A11 levels. Cell proliferation, colony formation, lipid reactive oxygen species (ROS), MDA concentration, 4-HNE, GSH/GSSG ratio and cell death assays as well as subcutaneous xenograft experiments were used to elucidate the effects of SLC7A11 in HB cell proliferation and ferroptosis. Furthermore, MeRIP-qPCR, dual luciferase reporter, RNA pulldown, RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) and RACE-PAT assays were performed to elucidate the underlying mechanism through which SLC7A11 was regulated by the m6A modification in HB.
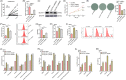
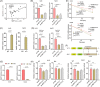
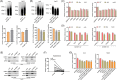
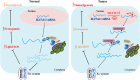
Results: SLC7A11 expression was highly upregulated in HB. SLC7A11 upregulation promoted HB cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo, inhibiting HB cell ferroptosis. Mechanistically, SLC7A11 mRNA exhibited abnormal METTL3-mediated m6A modification, which enhanced its stability and expression. IGF2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1) was identified as the m6A reader of SLC7A11, enhancing SLC7A11 mRNA stability and expression by inhibiting SLC7A11 mRNA deadenylation in an m6A-dependent manner. Moreover, IGF2BP1 was found to block BTG2/CCR4-NOT complex recruitment via competitively binding to PABPC1, thereby suppressing SLC7A11 mRNA deadenylation.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrated that the METTL3-mediated SLC7A11 m6A modification enhances HB ferroptosis resistance. The METTL3/IGF2BP1/m6A modification promotes SLC7A11 mRNA stability and upregulates its expression by inhibiting the deadenylation process. Our study highlights a critical role of the m6A modification in SLC7A11-mediated ferroptosis, providing a potential strategy for HB therapy through blockade of the m6A-SLC7A11 axis.
Keywords: IGF2BP1; SLC7A11; ferroptosis; hepatoblastoma; m6A methylation; resistance.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Shanghai Institute of Clinical Bioinformatics.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
N6 -methyladenosine-RNA methylation promotes expression of solute carrier family 7 member 11, an uptake transporter of cystine for lipid reactive oxygen species scavenger glutathione synthesis, leading to hepatoblastoma ferroptosis resistance.Clin Transl Med. 2022 May;12(5):e889. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.889. Clin Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35604883 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Czauderna P, Lopez‐Terrada D, Hiyama E, Häberle B, Malogolowkin MH, Meyers RL. Hepatoblastoma state of the art: pathology, genetics, risk stratification, and chemotherapy. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2014;26(1):19‐28. - PubMed
-
- Zhang YT, Feng LH, Zhong XD, Wang LZ, Chang J. Single‐agent cisplatin treatment of children with high‐risk hepatoblastoma. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2014;36(4):271‐275. - PubMed
-
- Uchida H, Sakamoto S, Sasaki K, et al. Surgical treatment strategy for advanced hepatoblastoma: resection versus transplantation. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2018;65(12):e27383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
