Integrated genomics and chemical biology herald an era of sophisticated antibacterial discovery, from defining essential genes to target elucidation
- PMID: 35523184
- PMCID: PMC9893512
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2022.04.006
Integrated genomics and chemical biology herald an era of sophisticated antibacterial discovery, from defining essential genes to target elucidation
Abstract
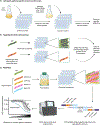
The golden age of antibiotic discovery in the 1940s-1960s saw the development and deployment of many different classes of antibiotics, revolutionizing the field of medicine. Since that time, our ability to discover antibiotics of novel structural classes or mechanisms has not kept pace with the ever-growing threat of antibiotic resistance. Recently, advances at the intersection of genomics and chemical biology have enabled efforts to better define the vulnerabilities of essential gene targets, to develop sophisticated whole-cell chemical screening methods that reveal target biology early, and to elucidate small molecule targets and modes of action more effectively. These new technologies have the potential to expand the chemical diversity of antibiotic candidates, as well as the breadth of targets. We illustrate how the latest tools of genomics and chemical biology are being integrated to better understand pathogen vulnerabilities and antibiotic mechanisms in order to inform a new era of antibiotic discovery.
Keywords: antibiotic discovery; gene essentiality; high-throughput screen; mode of action; target.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
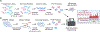

Similar articles
-
Systems-Level Chemical Biology to Accelerate Antibiotic Drug Discovery.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Apr 20;54(8):1909-1920. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00011. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 33787225 Review.
-
Small and lethal: searching for new antibacterial compounds with novel modes of action.Biochem Cell Biol. 2008 Apr;86(2):111-5. doi: 10.1139/O08-011. Biochem Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18443624 Review.
-
Novel antibacterials: a genomics approach to drug discovery.Curr Drug Targets Infect Disord. 2002 Dec;2(4):291-308. doi: 10.2174/1568005023342227. Curr Drug Targets Infect Disord. 2002. PMID: 12570737 Review.
-
The role of genomics in the discovery of novel targets for antibiotic therapy.Pharmacogenomics. 2002 May;3(3):315-23. doi: 10.1517/14622416.3.3.315. Pharmacogenomics. 2002. PMID: 12052140 Review.
-
When will the genomics investment pay off for antibacterial discovery?Biochem Pharmacol. 2006 Mar 30;71(7):1096-102. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2005.11.025. Epub 2006 Jan 4. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16387281 Review.
Cited by
-
Primed for Discovery.Biochemistry. 2024 Nov 5;63(21):2705-2713. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.4c00464. Epub 2024 Oct 15. Biochemistry. 2024. PMID: 39497571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Vibrio parahaemolyticus compounds from Streptomyces parvus based on Pan-genome and subtractive proteomics.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jul 6;14:1218176. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1218176. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37485508 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

