The N-Terminus of Human Sulfotransferase 2B1b─a Sterol-Sensing Allosteric Site
- PMID: 35523209
- PMCID: PMC9260854
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.1c00740
The N-Terminus of Human Sulfotransferase 2B1b─a Sterol-Sensing Allosteric Site
Abstract
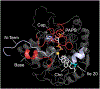
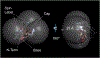
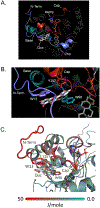
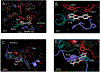
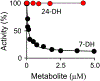
Among human cytosolic sulfotransferases, SULT2B1b is highly specific for oxysterols─oxidized cholesterol derivatives, including nuclear-receptor ligands causally linked to skin and neurodegerative diseases, cancer and atherosclerosis. Sulfonation of signaling oxysterols redirects their receptor-binding functions, and controlling these functions is expected to prove valuable in disease prevention and treatment. SULT2B1b is distinct among the human SULT2 isoforms by virtue of its atypically long N-terminus, which extends 15 residues beyond the next longest N-terminus in the family. Here, in silico studies are used to predict that the N-terminal extension forms an allosteric pocket and to identify potential allosteres. One such allostere, quercetin, is used to confirm the existence of the pocket and to demonstrate that allostere binding inhibits turnover. The structure of the pocket is obtained by positioning quercetin on the enzyme, using spin-label-triangulation NMR, followed by NMR distance-constrained molecular dynamics docking. The model is confirmed using a combination of site-directed mutagenesis and initial-rate studies. Stopped-flow ligand-binding studies demonstrate that inhibition is achieved by stabilizing the closed form of the enzyme active-site cap, which encapsulates the nucleotide, slowing its release. Finally, endogenous oxysterols are shown to bind to the site in a highly selective fashion─one of the two immediate biosynthetic precursors of cholesterol (7-dehydrocholesterol) is an inhibitor, while the other (24-dehydrocholesterol) is not. These findings provide insights into the allosteric dialogue in which SULT2B1b participates in in vivo and establishes a template against which to develop isoform-specific inhibitors to control SULT2B1b biology.
Figures

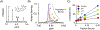
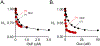
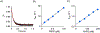
Similar articles
-
Sulfotransferase 2B1b, Sterol Sulfonation, and Disease.Pharmacol Rev. 2023 May;75(3):521-531. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.122.000679. Epub 2022 Dec 22. Pharmacol Rev. 2023. PMID: 36549865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The NSAID allosteric site of human cytosolic sulfotransferases.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 8;292(49):20305-20312. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.817387. Epub 2017 Oct 16. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 29038294 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of hydroxysteroid sulfotransferase 2B1b promotes hepatic oval cell proliferation by modulating oxysterol-induced LXR activation in a mouse model of liver injury.Arch Toxicol. 2017 Jan;91(1):271-287. doi: 10.1007/s00204-016-1693-z. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Arch Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27052460
-
Site-directed mutagenesis of human cytosolic sulfotransferase (SULT) 2B1b to phospho-mimetic Ser348Asp results in an isoform with increased catalytic activity.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2011 Nov;127(3-5):315-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2011.07.010. Epub 2011 Aug 6. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21855633 Free PMC article.
-
SULT2B1: unique properties and characteristics of a hydroxysteroid sulfotransferase family.Drug Metab Rev. 2013 Nov;45(4):388-400. doi: 10.3109/03602532.2013.835609. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Drug Metab Rev. 2013. PMID: 24020383 Review.
Cited by
-
Sulfotransferase 2B1b, Sterol Sulfonation, and Disease.Pharmacol Rev. 2023 May;75(3):521-531. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.122.000679. Epub 2022 Dec 22. Pharmacol Rev. 2023. PMID: 36549865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytosolic sulfotransferases in endocrine disruption.Essays Biochem. 2024 Dec 4;68(4):541-553. doi: 10.1042/EBC20230101. Essays Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38699885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex roles for sulfation in the toxicities of polychlorinated biphenyls.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024 Feb;54(2):92-122. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2024.2311270. Epub 2024 Feb 16. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38363552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human sulfotransferase SULT2B1 physiological role and the impact of genetic polymorphism on enzyme activity and pathological conditions.Front Genet. 2024 Aug 30;15:1464243. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1464243. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39280099 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mesiano S, and Jaffe RB (1997) Developmental and functional biology of the primate fetal adrenal cortex., Endocr Rev 18, 378–403. - PubMed
-
- Li L, and Falany CN (2007) Elevated hepatic SULT1E1 activity in mouse models of cystic fibrosis alters the regulation of estrogen responsive proteins, J Cyst Fibros 6, 23–30. - PubMed
-
- Cook IT, Duniac-Dmuchowski Z, Kocarek TA, Runge-Morris M, and Falany CN (2009) 24-Hydroxycholesterol Sulfation by Human Cytosolic Sulfotransferases: Formation of Monosulfates and Disulfates, Molecular Modeling, Sulfatase Sensitivity and Inhibition of LXR Activation, Drug Metab Dispos 37, 2069–2078. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

