Neurite Exchange Imaging (NEXI): A minimal model of diffusion in gray matter with inter-compartment water exchange
- PMID: 35523369
- PMCID: PMC10363376
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2022.119277
Neurite Exchange Imaging (NEXI): A minimal model of diffusion in gray matter with inter-compartment water exchange
Abstract
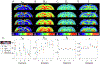
Biophysical models of diffusion in white matter have been center-stage over the past two decades and are essentially based on what is now commonly referred to as the "Standard Model" (SM) of non-exchanging anisotropic compartments with Gaussian diffusion. In this work, we focus on diffusion MRI in gray matter, which requires rethinking basic microstructure modeling blocks. In particular, at least three contributions beyond the SM need to be considered for gray matter: water exchange across the cell membrane - between neurites and the extracellular space; non-Gaussian diffusion along neuronal and glial processes - resulting from structural disorder; and signal contribution from soma. For the first contribution, we propose Neurite Exchange Imaging (NEXI) as an extension of the SM of diffusion, which builds on the anisotropic Kärger model of two exchanging compartments. Using datasets acquired at multiple diffusion weightings (b) and diffusion times (t) in the rat brain in vivo, we investigate the suitability of NEXI to describe the diffusion signal in the gray matter, compared to the other two possible contributions. Our results for the diffusion time window 20-45 ms show minimal diffusivity time-dependence and more pronounced kurtosis decay with time, which is well fit by the exchange model. Moreover, we observe lower signal for longer diffusion times at high b. In light of these observations, we identify exchange as the mechanism that best explains these signal signatures in both low-b and high-b regime, and thereby propose NEXI as the minimal model for gray matter microstructure mapping. We finally highlight multi-b multi-t acquisition protocols as being best suited to estimate NEXI model parameters reliably. Using this approach, we estimate the inter-compartment water exchange time to be 15 - 60 ms in the rat cortex and hippocampus in vivo, which is of the same order or shorter than the diffusion time in typical diffusion MRI acquisitions. This suggests water exchange as an essential component for interpreting diffusion MRI measurements in gray matter.
Keywords: Cell membrane permeability; Cortex; Diffusion MRI; Exchange; Gray matter; Microstructure.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest None.
Figures

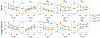
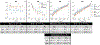
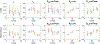
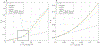
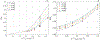
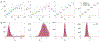
References
-
- Andersson M, Kjer HM, Rafael-Patino J, Pacureanu A, Pakkenberg B, Thiran JP, Ptito M, Bech M, Dahl AB, Dahl VA, Dyrby TB, 2020. Axon morphology is modulated by the local environment and impacts the noninvasive investigation of its structure–function relationship. PNAS 117, 33649–33659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2012533117. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

