Interim results from a postmarketing surveillance study of patients with FLT3-mutated relapsed/refractory AML treated with the FLT3 inhibitor gilteritinib in Japan
- PMID: 35523692
- PMCID: PMC9264337
- DOI: 10.1093/jjco/hyac069
Interim results from a postmarketing surveillance study of patients with FLT3-mutated relapsed/refractory AML treated with the FLT3 inhibitor gilteritinib in Japan
Erratum in
-
Correction.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2022 Nov 3;52(11):1358. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyac156. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36124846 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: Gilteritinib received approval for the treatment of FLT3-mutated relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia in Japan in 2018. In accordance with regulatory requirements, we conducted a multicenter, observational surveillance of gilteritinib use in Japan.
Methods: Patients were followed for 6 months from gilteritinib treatment initiation. The primary endpoint of the surveillance was incidence of adverse drug reactions related to each element of the safety specification defined in the Japanese Risk Management Plan. This interim analysis presents data collected from 3 December 2018 to 20 September 2020.
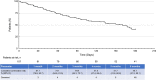
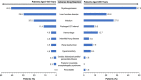
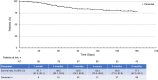
Results: Among 204 patients with case report forms, 107 consented to data publication. Of these 107 patients, 59.8% (n = 64) were male and 58.9% (n = 63) were aged ≥65 years; most received a 120-mg/day initial (80.4%; 86/107) and maximum (74.8%; 80/107) daily dose. The discontinuation rate was 61.7% (66/107); the most common reasons for discontinuation were disease progression (18.7%), transplantation (16.8%) and adverse events (15.0%). The adverse drug reaction rate was 77.6%. The incidences of adverse drug reactions (grade ≥ 3) related to each element of the safety specification were myelosuppression, 44.9% (38.3%); liver function disorder, 24.3% (6.5%); infections, 24.3% (21.5%); prolonged QT interval, 10.3% (2.8%); hemorrhage, 9.3% (6.5%); renal dysfunction, 6.5% (0); hypersensitivity, 5.6% (1.9%); interstitial lung disease, 4.7% (3.7%); cardiac failure/pericarditis/pericardial effusion, 1.9% (0.9%); pancreatitis, 0.9% (0); posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, 0.9% (0.9%). The composite complete remission rate was 62.7%; the 6-month overall survival rate was 77.7%.
Conclusion: Gilteritinib treatment for 6 months in Japan was associated with acceptable efficacy and no new safety concerns were observed.
Keywords: fms-like tyrosine kinase 3; acute myeloid leukemia; adverse drug reaction.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
References
-
- Röllig C, Serve H, Huttmann A, et al. Addition of sorafenib versus placebo to standard therapy in patients aged 60 years or younger with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukaemia (SORAML): a multicentre, phase 2, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 2015;16:1691–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

