Surrogate cytokine agonists: promising agents against COVID-19
- PMID: 35523768
- PMCID: PMC9072766
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-022-01015-w
Surrogate cytokine agonists: promising agents against COVID-19
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing interests.
Figures
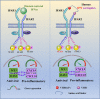
Comment on
-
Facile discovery of surrogate cytokine agonists.Cell. 2022 Apr 14;185(8):1414-1430.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.02.025. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Cell. 2022. PMID: 35325595 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

