The roles of osteoprotegerin in cancer, far beyond a bone player
- PMID: 35523775
- PMCID: PMC9076607
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-022-01042-0
The roles of osteoprotegerin in cancer, far beyond a bone player
Abstract
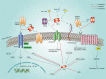
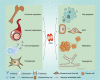
Osteoprotegerin (OPG), also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 11B (TNFRSF11B), is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily. Characterized by its ability to bind to receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand (RANKL), OPG is critically involved in bone remodeling. Emerging evidence implies that OPG is far beyond a bone-specific modulator, and is involved in multiple physiological and pathological processes, such as immunoregulation, vascular function, and fibrosis. Notably, numerous preclinical and clinical studies have been conducted to assess the participation of OPG in tumorigenesis and cancer development. Mechanistic studies have demonstrated that OPG is involved in multiple hallmarks of cancer, including tumor survival, epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT), neo-angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis. In this review, we systematically summarize the basis and advances of OPG from its molecular structure to translational applications. In addition to its role in bone homeostasis, the physiological and pathological impacts of OPG on human health and its function in cancer progression are reviewed, providing a comprehensive understanding of OPG. We aim to draw more attention to OPG in the field of cancer, and to propose it as a promising diagnostic or prognostic biomarker as well as potential therapeutic target for cancer.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

