Irisin protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury via attenuating AMPK mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress
- PMID: 35523819
- PMCID: PMC9076689
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-11343-0
Irisin protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury via attenuating AMPK mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress
Abstract
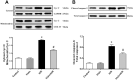
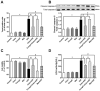
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress plays a central role in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. Irisin has been reported to have protective properties in ischemia disease. In this study, we aimed at investigating whether irisin could alleviate myocardial I/R injury by ER stress attenuation. The in vitro model of hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) was established, which resembles I/R in vivo. Cell viability and apoptosis were estimated. Expressions of cleaved caspase-3, cytochrome c, GRP78, pAMPK, CHOP, and eIF2α were assessed by western blot. Our results revealed that pre-treatment with irisin significantly decreased cytochrome c release from mitochondria and caspase-3 activation caused by H/R. Irsin also reduced apoptosis and increased cell viability. These effects were abolished by AMPK inhibitor compound C pre-treatment. Also, GRP78 and CHOP expressions were up-regulated in the H/R group compared to the control group; however, irisin attenuated their expression. The pAMPK level was significantly decreased compared to the control, and this effect could be partly reversed by metformin pre-treatment. These results suggest that ER stress is associated with cell viability decreasing and cardiomyocytes apoptosis induced by H/R. Irisin could efficiently protect cardiomyocytes from H/R-injury via attenuating ER stress and ER stress-induced apoptosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

