Preventing erosion of X-chromosome inactivation in human embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 35523820
- PMCID: PMC9076865
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-30259-x
Preventing erosion of X-chromosome inactivation in human embryonic stem cells
Abstract
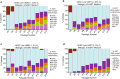
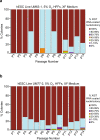
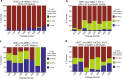
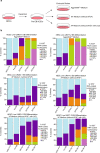
X-chromosome inactivation is a paradigm of epigenetic transcriptional regulation. Female human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) often undergo erosion of X-inactivation upon prolonged culture. Here, we investigate the sources of X-inactivation instability by deriving new primed pluripotent hESC lines. We find that culture media composition dramatically influenced the expression of XIST lncRNA, a key regulator of X-inactivation. hESCs cultured in a defined xenofree medium stably maintained XIST RNA expression and coating, whereas hESCs cultured in the widely used mTeSR1 medium lost XIST RNA expression. We pinpointed lithium chloride in mTeSR1 as a cause of XIST RNA loss. The addition of lithium chloride or inhibitors of GSK-3 proteins that are targeted by lithium to the defined hESC culture medium impeded XIST RNA expression. GSK-3 inhibition in differentiating female mouse embryonic stem cells and epiblast stem cells also resulted in a loss of XIST RNA expression. Together, these data may reconcile observed variations in X-inactivation in hESCs and inform the faithful culture of pluripotent stem cells.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Human Naive Pluripotent Stem Cells Model X Chromosome Dampening and X Inactivation.Cell Stem Cell. 2017 Jan 5;20(1):87-101. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2016.10.006. Epub 2016 Dec 15. Cell Stem Cell. 2017. PMID: 27989770 Free PMC article.
-
Large-Scale Analysis of X Inactivation Variations between Primed and Naïve Human Embryonic Stem Cells.Cells. 2022 May 24;11(11):1729. doi: 10.3390/cells11111729. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35681423 Free PMC article.
-
Xist deficiency and disorders of X-inactivation in rabbit embryonic stem cells can be rescued by transcription-factor-mediated conversion.Stem Cells Dev. 2014 Oct 1;23(19):2283-96. doi: 10.1089/scd.2014.0011. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Stem Cells Dev. 2014. PMID: 24805295 Free PMC article.
-
Activators and repressors: A balancing act for X-inactivation.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016 Aug;56:3-8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.05.005. Epub 2016 May 17. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27223409 Review.
-
The Ambivalent Role of lncRNA Xist in Carcinogenesis.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2019 Apr;15(2):314-323. doi: 10.1007/s12015-019-9871-z. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2019. PMID: 30685833 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene reactivation upon erosion of X chromosome inactivation in female hiPSCs is predictable yet variable and persists through differentiation.Stem Cell Reports. 2025 May 13;20(5):102472. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2025.102472. Epub 2025 Apr 3. Stem Cell Reports. 2025. PMID: 40185090 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging X-linked genes associated with neurodevelopmental disorders in females.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2024 Oct;88:102902. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2024.102902. Epub 2024 Aug 20. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39167997 Review.
-
Lineage-specific dynamics of loss of X upregulation during inactive-X reactivation.Stem Cell Reports. 2024 Nov 12;19(11):1564-1582. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2024.10.001. Epub 2024 Oct 31. Stem Cell Reports. 2024. PMID: 39486405 Free PMC article.
-
Modelling human brain development and disease with organoids.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2025 May;26(5):389-412. doi: 10.1038/s41580-024-00804-1. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 39668188 Review.
-
SeqVerify: An accessible analysis tool for cell line genomic integrity, contamination, and gene editing outcomes.Stem Cell Reports. 2024 Oct 8;19(10):1505-1515. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2024.08.004. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Stem Cell Reports. 2024. PMID: 39270651 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

