Whole genome sequencing and analysis of fenvalerate degrading bacteria Citrobacter freundii CD-9
- PMID: 35523901
- PMCID: PMC9076782
- DOI: 10.1186/s13568-022-01392-z
Whole genome sequencing and analysis of fenvalerate degrading bacteria Citrobacter freundii CD-9
Abstract
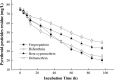
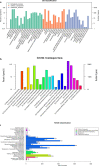
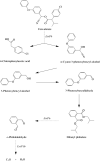
Citrobacter freundii CD-9 is a Gram-negative bacteria sourced from factory sludge that can use fenvalerate as its sole carbon source and has a broad degradation spectrum for pyrethroid pesticides. The whole genome of CD-9 sequenced using Illumina HiSeq PE150 was reported in this study. The CD-9 genome size was 5.33 Mb and the G + C content was 51.55%. A total of 5291 coding genes, 9 5s-rRNA, and 79 tRNA were predicted bioinformatically. 3586 genes annotated to the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database that can be involved in 173 metabolic pathways, including various microbial metabolic pathways that degrade exogenous chemicals, especially those that degrade aromatic compounds, and also produce a variety of bioactive substances. Fifty genes related to pyrethroid degradation were identified in the C. freundii CD-9 genome, including 9 dioxygenase, 25 hydrolase, and 16 esterase genes. Notably, RT-qPCR results showed that from the predicted 13 genes related to fenvalerate degradation, the expression of six genes, including esterase, HAD family hydrolase, lipolytic enzyme, and gentisic acid dioxygenase, was induced in the presence of fenvalerate. In this study, the key genes and degradation mechanism of C. freundii CD-9 were analyzed and the results provide scientific evidence to support its application in environmental bioremediation. It can establish application models for different environmental pollution management by constructing genetically engineered bacteria for efficient fenvalerate or developing enzyme formulations that can be industrially produced.
Keywords: Bioremediation; Genomics; Pyrethroids; RT-qPCR.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Arbeli Z, Fuentes CL. Accelerated biodegradation of pesticides: an overview of the phenomenon, its basis and possible solutions; and a discussion on the tropical dimension. Crop Prot. 2007;26(12):1733–1746. doi: 10.1016/j.cropro.2007.03.009. - DOI
-
- Aregbesola OA, Kumar A, Mokoena MP, Olaniran AO. Whole-genome sequencing, genome mining, metabolic reconstruction and evolution of pentachlorophenol and other xenobiotic degradation pathways in Bacillus tropicus strain AOA-CPS1. Funct Integr Genomics. 2021;21(2):171–193. doi: 10.1007/s10142-021-00768-x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ashburner M, Ball AC, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genet. 2000;25(1):25–29. doi: 10.1038/75556. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 32102094/National Nature Science Foundation of China
- 2019YJ0389/Application Foundation Project of Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology
- No. 2019ZYZF0170/Science and Technology Support Project of Sichuan Province
- 2018-YF05-00522-SN/Technological Innovation Project of Chengdu Science and Technology Bureau
- Z1310525/Key Scientific Research Fund of Xihua University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

