Prevalence of inflicted and neglectful femur shaft fractures in young children in national level I trauma centers
- PMID: 35523968
- PMCID: PMC9616777
- DOI: 10.1007/s00247-022-05378-8
Prevalence of inflicted and neglectful femur shaft fractures in young children in national level I trauma centers
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of inflicted femur fractures in young children varies (1.5-35.2%), but these data are based on small retrospective studies with high heterogeneity. Age and mobility of the child seem to be indicators of inflicted trauma.
Objective: This study describes other factors associated with inflicted and neglectful trauma that can be used to distinguish inflicted and neglectful from accidental femur fractures.
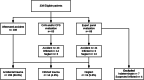
Materials and methods: This retrospective study included children (0-6 years) who presented with an isolated femur fracture at 1 of the 11 level I trauma centers in the Netherlands between January 2010 and January 2016. Outcomes were classified based on the conclusions of the Child Abuse and Neglect teams or the court. Cases in which conclusions were unavailable and there was no clear accidental cause were reviewed by an expert panel.
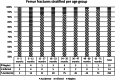
Results: The study included 328 children; 295 (89.9%) cases were classified as accidental trauma. Inflicted trauma was found in 14 (4.3%), while 19 (5.8%) were cases of neglect. Indicators of inflicted trauma were age 0-5 months (29%, positive likelihood ratio [LR +] 8.35), 6-12 months (18%, LR + 5.98) and 18-23 months (14%, LR + 3.74). Indicators of neglect were age 6-11 months (18%, LR + 4.41) and age 18-23 months (8%, LR + 1.65). There was no difference in fracture morphology among groups.
Conclusion: It is unlikely that an isolated femur fracture in ambulatory children age > 24 months is caused by inflicted trauma/neglect. Caution is advised in children younger than 24 months because that age is the main factor associated with inflicted trauma/neglect and inflicted femur fractures.
Keywords: Child abuse; Children; Femur; Fractures; Infants; Inflicted trauma; Radiography.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
References
-
- American College of Surgeons (2022) Clarification document: resources for optimal care of the injured patient 2014 standards. https://www.facs.org/-/media/files/quality-programs/trauma/vrc-resources.... Accessed 03 Mar 2022
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous