Oral health knowledge and oral hygiene practice among visually impaired subjects in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
- PMID: 35524206
- PMCID: PMC9077845
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-022-02199-x
Oral health knowledge and oral hygiene practice among visually impaired subjects in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Abstract
Background: Oral health is a global issue. It has an enormous impact on the overall health and well-being of an individual. In addition, many studies indicate visual impairment as one of the constraints for proper maintenance of oral hygiene. However, little is known about visually impaired individuals' oral health knowledge and behavior in Ethiopia, specifically in Addis Ababa. Therefore, this study is conducted to assess the oral health knowledge and related behaviors among participants with visual impairment in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
Aim: This study aimed to assess the oral health knowledge and oral hygiene practice among visually impaired participants in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. It is initially imperative to recognize the deficiency of data regarding the dental health care and needs of such visually impaired individuals in Ethiopia.
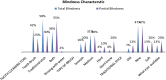
Methods: It is a quantitative cross-section study design carried out at the Ethiopian National Association for the blind, located in Addis Ababa, the capital city of Ethiopia. A survey was conducted by convenience sampling of visually impaired library attendees' at the blind association. Sixty-five individuals, of which 46 males and 19 females, agreed to take part in the study. Of these, 30.8% had partial and 69.2% total visual impairment.
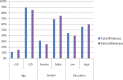
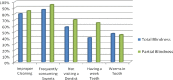
Results: 61.3% with totally and 72% with partially visually impaired scored high in the knowledge of caries causes respectively. The use of tooth brushing was confirmed by 42.2% with totally and 25% with partially visually impaired. The use of Traditional chewing sticks was confirmed by 57.7% with totally and 30% with partially visually impaired individuals. Moreover, both (Toothbrush and Traditional chewing stick) was used by 35.5% totally and 55% partially visually impaired individuals, respectively.
Conclusions: The study showed the awareness about the causes of dental caries among the visually impaired was high. However, the majority of them had a significant misconception about the causes of dental caries.
Keywords: Chewing stick; Oral health knowledge; Tooth brushing; Visual impairment.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oral health status, knowledge, attitudes and behaviours among marginalized children in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.J Child Health Care. 2016 Jun;20(2):252-61. doi: 10.1177/1367493515569328. Epub 2015 Feb 23. J Child Health Care. 2016. PMID: 25713009
-
Improvement of oral health knowledge in a group of visually impaired students.Oral Health Prev Dent. 2006;4(4):243-53. Oral Health Prev Dent. 2006. PMID: 17153646
-
Comparative study of the oral hygiene status of users of mefakia (traditional tooth cleaning method) and modern toothbrushes among patients at the Holy Bethel Dental Clinic in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.BDJ Open. 2024 Dec 28;10(1):99. doi: 10.1038/s41405-024-00290-9. BDJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39732717 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions in improving the oral hygiene of visually impaired individuals: A systematic review.Health Soc Care Community. 2022 Jul;30(4):e1092-e1100. doi: 10.1111/hsc.13517. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Health Soc Care Community. 2022. PMID: 34309125
-
Oral health status and dental care for individuals with visual impairment. A narrative review.Spec Care Dentist. 2023 Mar;43(2):221-231. doi: 10.1111/scd.12764. Epub 2022 Aug 8. Spec Care Dentist. 2023. PMID: 35941095 Review.
Cited by
-
Oral health status and hygiene practices among visually impaired adolescents from a school in Kenya.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Oct 7;23(1):725. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03428-7. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37805471 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Oral Hygiene-Related Mobile Apps for Children in Sub-Saharan Africa.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 1;19(19):12565. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912565. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36231862 Free PMC article.
-
Association between health literacy and health-promoting behaviors in individuals with visual impairments.J Educ Health Promot. 2025 Jul 4;14:245. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_1383_24. eCollection 2025. J Educ Health Promot. 2025. PMID: 40772091 Free PMC article.
-
Caries Experience and Oral Health-Related Habits in Blind and Low-Vision Individuals in Croatia.J Clin Med. 2025 Aug 7;14(15):5576. doi: 10.3390/jcm14155576. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40807195 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of dental health and salivary microbiota characteristics of children with visual impairment in Guangzhou, China.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Mar 19;25(1):408. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-05713-z. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40108579 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Oral Health Fact Sheet No 318; 2007.
-
- Dye BA, Tan S, Smia Y, Lewis BG, Barker LK, Thornton Evan G, et al. Trends in oral health status: United States, 1988–1994 and 1999–2004. National Center for Health Statistics. Vital Health Stat. 2007;11(248):1–92. - PubMed
-
- Kasi SV, Cobbs S. Health behavior, illness behavior and sick role behavior. Arch Environ Health. 1996;12:246–266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

