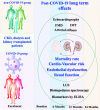
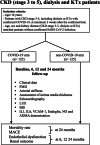
Long-term cardio-vascular risk assessment in chronic kidney disease and kidney transplanted patients following SARS-COV-2 disease: protocol for multi-center observational match controlled trial
- PMID: 35524223
- PMCID: PMC9077937
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-022-02809-4
Long-term cardio-vascular risk assessment in chronic kidney disease and kidney transplanted patients following SARS-COV-2 disease: protocol for multi-center observational match controlled trial
Abstract
Background: The coronavirus disease (COVID-19) caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) produced a pandemic since March 2020 by affecting more than 243 million people with more than 5 million deaths globally. SARS-CoV-2 infection is produced by binding to angiotensin-converting enzyme, which among other sites is highly expressed in the endothelial cells of the blood vessels, pericytes and the heart, as well as in renal podocytes and proximal tubular epithelial cells. SARS-CoV-2 and cardiovascular disease (CVD) are interconnected by risk factors association with an increased incidence of the disease and by determining de novo cardiac complications. At the same time, COVID-19 disease can lead to acute kidney injury directly, or due to sepsis, multi-organ failure and shock. Therefore, the pre-existence of both CVD and chronic kidney disease (CKD) is linked with a higher risk of severe disease and worse prognosis.
Methods: The main aim of this study is to assess the CV risk in a CKD (stage 3 to 5), dialysis and kidney transplanted population, following SARS-CoV-2 infection, with focus on the endothelial dysfunction as compared to a control group of matched patients. By using clinical evaluation, flow-mediated dilatation, carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity, intima-media thickness, echocardiographic parameters, lung ultrasound, bioimpedance spectroscopy and a series of novel biomarkers, the investigators will determine the long-term impact of this disease on CV and renal outcomes.
Discussion: This study will address the challenges and implications in long-term CV sequeale of COVID-19 and focus on a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms and possible therapeutic options.
Trial registration: Patient enrolment in the trial started in January 2021 and is expected to finish at the end of 2022. The study can be found on ClinicalTrials.gov database with NCT05125913 identifier. Registered on 18 November 2021 - Retrospectively registered.
Keywords: Cardio-vascular risk; Cardiovascular disease; Chronic kidney disease; Kidney transplant; SARS-CoV-2; dialysis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-term efficacy and safety of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in patients with chronic kidney disease, on dialysis or after kidney transplantation: a national prospective observational cohort study.BMC Nephrol. 2022 Feb 5;23(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s12882-022-02680-3. BMC Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35123437 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and Efficacy of Imatinib for Hospitalized Adults with COVID-19: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Oct 28;21(1):897. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04819-9. Trials. 2020. PMID: 33115543 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of hydroxychloroquine for post-exposure prophylaxis to prevent severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection among adults exposed to coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Jun 3;21(1):475. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04446-4. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32493478 Free PMC article.
-
The Significance of Endothelial Dysfunction in Long COVID-19 for the Possible Future Pandemic of Chronic Kidney Disease and Cardiovascular Disease.Biomolecules. 2024 Aug 8;14(8):965. doi: 10.3390/biom14080965. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39199353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 and cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic kidney disease.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2024 Jan 31;39(2):177-189. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfad170. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2024. PMID: 37771078 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Prior COVID-19 on Long-Term Mortality and Echocardiographic Predictors in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Mar 10;15(6):678. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15060678. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150021 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Evolution of Post-COVID-19 Echocardiographic Parameters in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Prospective Comparative Observational Study.J Clin Med. 2025 Mar 8;14(6):1823. doi: 10.3390/jcm14061823. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40142631 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ghebreyesus TA. WHO director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19-11 March 2020. Geneva: WHO; 2020.
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available from: https://covid19.who.int/ (Accessed 26 Oct 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous