Triglyceride-glucose index as a marker in cardiovascular diseases: landscape and limitations
- PMID: 35524263
- PMCID: PMC9078015
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-022-01511-x
Triglyceride-glucose index as a marker in cardiovascular diseases: landscape and limitations
Abstract
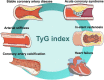
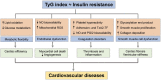
The triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index has been identified as a reliable alternative biomarker of insulin resistance (IR). Recently, a considerable number of studies have provided robust statistical evidence suggesting that the TyG index is associated with the development and prognosis of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Nevertheless, the application of the TyG index as a marker of CVD has not systemically been evaluated, and even less information exists regarding the underlying mechanisms associated with CVD. To this end, in this review, we summarize the history of the use of the TyG index as a surrogate marker for IR. We aimed to highlight the application value of the TyG index for a variety of CVD types and to explore the potential limitations of using this index as a predictor for cardiovascular events to improve its application value for CVD and provide more extensive and precise supporting evidence.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Insulin resistance; Triglyceride-glucose index.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Sacco RL, Roth GA, Reddy KS, Arnett DK, Bonita R, Gaziano TA, Heidenreich PA, Huffman MD, Mayosi BM, Mendis S, et al. The heart of 25 by 25: achieving the goal of reducing global and regional premature deaths from cardiovascular diseases and stroke: a modeling study from the American Heart Association and World Heart Federation. Circulation. 2016;133(23):e674–690. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000395. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

