Oral lichen planus: comparative efficacy and treatment costs-a systematic review
- PMID: 35524296
- PMCID: PMC9074269
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-022-02168-4
Oral lichen planus: comparative efficacy and treatment costs-a systematic review
Abstract
Objective: To compare the reported efficacy and costs of available interventions used for the management of oral lichen planus (OLP).
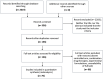
Materials and methods: A systematic literature search was performed from database inception until March 2021 in MEDLINE via PubMed and the Cochrane library following PRISMA guidelines. Only randomized controlled trials (RCT) comparing an active intervention with placebo or different active interventions for OLP management were considered.
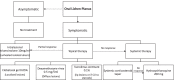
Results: Seventy (70) RCTs were included. The majority of evidence suggested efficacy of topical steroids (dexamethasone, clobetasol, fluocinonide, triamcinolone), topical calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus, pimecrolimus, cyclosporine), topical retinoids, intra-lesional triamcinolone, aloe-vera gel, photodynamic therapy, and low-level laser therapies for OLP management. Based on the estimated cost per month and evidence for efficacy and side-effects, topical steroids (fluocinonide > dexamethasone > clobetasol > triamcinolone) appear to be more cost-effective than topical calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus > pimecrolimus > cyclosporine) followed by intra-lesional triamcinolone.
Conclusion: Of common treatment regimens for OLP, topical steroids appear to be the most economical and efficacious option followed by topical calcineurin inhibitors. Large-scale multi-modality, prospective trials in which head-to-head comparisons interventions are compared are required to definitely assess the cost-effectiveness of OLP treatments.
Keywords: Cost; Critical review; Efficacy; Oral lichen planus; Treatment.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Wang D, Sandhu S, Woo SB. A guide for dental practitioners of common oral potentially malignant disorders. CDA J 2021;49.
-
- Oberti L, Gabrione F, Lucchese A, Di Stasio D, Carinci F, Lauritano D. Treatment of oral lichen planus: a narrative review. Front Physiol. 2019 doi: 10.3389/conf.fphys.2019.27.00004. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical